La révolution dans l'industrie manufacturière ne consiste pas simplement à appliquer des solutions informatiques aux processus existants, mais plutôt à créer un écosystème dynamique et intégré, alimenté par solutions de fabrication numérique où la vitesse, la précision et la flexibilité sont primordiales. L'intégration de technologies avancées telles que le big data, IoT, AI et ML n'est pas seulement une phase complémentaire mais une pierre angulaire, changeant fondamentalement la façon dont les usines fonctionnent et les produits sont fabriqués. Les prévisions pour le marché indique une hausse significative, passant de 307,87 milliards d'USD en 2023 à 733,75 milliards d'USD en 2028.
Au milieu de cette expansion technologique, il est essentiel de distinguer les éléments suivants solutions de fabrication numérique aura l'impact le plus profond sur l'efficacité des opérations et la réussite financière. Pour les entreprises confrontées à la transition vers le numérique, ce guide vise à réduire la complexité et à établir une feuille de route complète et claire, leur permettant d'exploiter tout le potentiel de la technologie.
AI, ML et IIoT
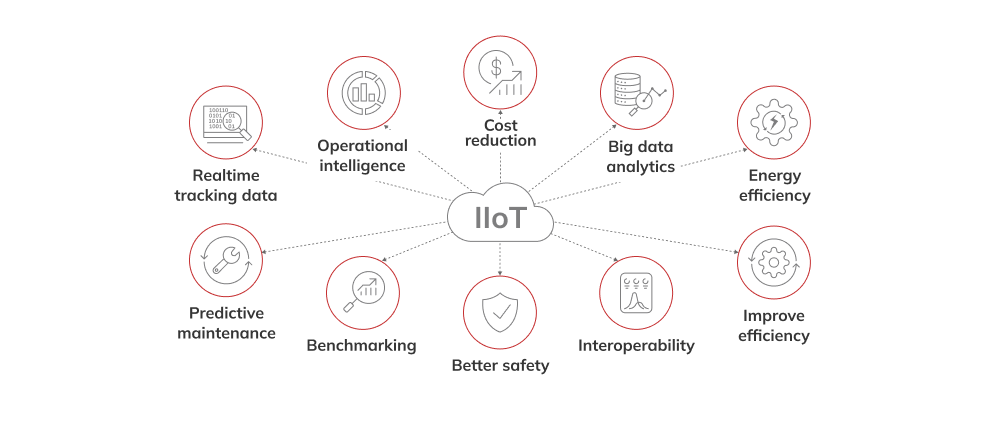
Alors que la vague du changement numérique déferle sur le secteur manufacturier, les rôles de l'intelligence artificielle (AI) et de l'apprentissage automatique (ML) sont de plus en plus imbriqués dans les opérations quotidiennes, reflétant l'impact généralisé de l'Internet industriel des objets (IIoT). Cette fusion repousse les limites des pratiques industrielles traditionnelles et la nature de la collaboration interindustrielle.
Le concept de l'IdO n'est pas une vision futuriste, mais plutôt une réalité actuelle qui est adoptée avec énergie par diverses industries. Selon une étude de Fortune Business InsightsLes entreprises du secteur de la santé et de l'industrie manufacturière sont également très actives dans ce domaine, l'agricultureLes technologies de l'information et de la communication, les transports, l'énergie et les télécommunications sont à l'avant-garde de l'intégration des solutions IdO en 2022.
Avec cette évolution vers les technologies de pointe, il vaut la peine de se pencher sur des exemples particuliers de la façon dont AI, ML et IoT sont utilisés dans ces domaines. Leur déploiement transforme les procédures standard en favorisant des stratégies préemptives pour aborder les problèmes, en fournissant une analyse immédiate des données et en formant la base de processus décisionnels profondément ancrés dans l'analyse des données.
Production intuitive dans l'industrie automobile
Faisons maintenant un zoom sur un secteur spécifique. L'industrie automobile fournit un exemple clair de la manière dont le AI et l'IIoT peuvent conduire à des processus de production plus intuitifs. Logiciel de fabrication numérique exploite les données des capteurs intégrés dans un réseau IIoT qui recueillent des données en temps réel sur tous les aspects, du positionnement des composants à l'efficacité des machines. Ces données sont examinées automatiquement par des algorithmes d'intelligence artificielle afin d'identifier les écarts et de prévenir les blocages, ce qui permet des interventions rapides qui maintiennent des normes strictes de sécurité et de qualité. Ce système permet non seulement d'affiner la précision de la production, mais aussi d'atténuer de manière proactive l'usure des machines, réduisant ainsi les temps morts et améliorant le rendement.
Cependant, cela va au-delà d'une simple surveillance de l'assemblage. Grâce aux capacités prédictives du AI, les flux de production peuvent être ajustés avec précision en fonction des fluctuations de la demande, ce qui se traduit par une chaîne d'approvisionnement souple et performante. Le domaine de l'assurance qualité a évolué de la même manière, avec logiciel de fabrication numérique avec des outils d'inspection visuelle compatibles AI qui examinent minutieusement les véhicules terminés par rapport à des points de référence précis. La fusion du AI avec l'IIoT surpasse les techniques de production de l'ancienne école, ouvrant la voie à une nouvelle ère d'efficacité améliorée où la production est affinée pour l'uniformité, l'excellence et l'adaptabilité à l'évolution du marché.
Assurance qualité, personnalisation et analyse prédictive
En passant du général au particulier, les systèmes AI dans l'industrie manufacturière ne se limitent pas à la maintenance prédictive. Dans la fabrication électronique, les algorithmes de AI et de ML examinent en permanence les micropuces et les cartes de circuits imprimés à des vitesses impossibles à atteindre pour les inspecteurs humains. Ils détectent les défauts microscopiques, garantissant ainsi un niveau élevé de qualité des produits. En outre, en tirant parti du AI et des données en direct de l'IIoT, si un modèle de smartphone spécifique connaît un pic soudain de la demande dans une région donnée, le calendrier de production peut être affiné pour amplifier la production de ce modèle, garantissant ainsi que l'offre s'aligne sur la demande.Le groupe BMW est un parfait exemple de la manière dont le AI et l'IIoT profitent à l'ensemble de l'industrie. Le AI contribue à l'automatisation des tâches de fabrication et de logistique, telles que les contrôles de qualité utilisant des données d'image. Les caméras sur la chaîne de montage capturent en permanence des images de produits, que les systèmes AI évaluent à la recherche de défauts, assurant ainsi un contrôle continu de la qualité. Cette technologie permet non seulement d'améliorer la qualité des produits, mais aussi d'alléger la charge de travail des employés.En outre, l'entreprise s'appuie sur la science des données pour garantir une prise de décision fondée sur les données. Par exemple, les capteurs recueillent des données d'état pour la maintenance des machines afin d'anticiper les pannes potentielles. Un indicateur tel qu'une consommation d'énergie élevée dans un système de convoyage peut signaler une usure, ce qui permet de remplacer les composants en temps voulu en se basant uniquement sur l'usure réelle.Améliorer l'intelligence opérationnelle dans l'industrie des boissons
L'application du AI et de l'IdO dépasse largement le domaine de la construction automobile. Appliquée à l'industrie des boissons, cette synthèse de AI et de l'IIoT continue de démontrer sa valeur. Les capteurs surveillent des paramètres tels que la consistance, les niveaux de pH et la température des boissons. Les prouesses analytiques de AI permettent de s'assurer que les boissons conservent un goût constant sur de vastes volumes de production. De plus, en analysant les tendances de consommation, AI peut anticiper les poussées de demande pour des boissons spécifiques, guidant ainsi les fabricants dans leurs stratégies de production.


Redéfinissez votre processus de fabrication grâce à nos solutions numériques innovantes.
Entrez dans l'ère de l'efficacité et de la précision pour améliorer votre production.
Robotique et automatisation avancées
La robotique est une autre technologie à la pointe de l'innovation technologique, qui élève le niveau de précision et d'efficacité de l'industrie manufacturière en transformant des machines statiques en acteurs polyvalents capables de s'adapter à des conditions changeantes en fonction des besoins. La robotique révolutionne l'industrie manufacturière, non seulement en améliorant la précision et le rendement, mais aussi en donnant aux robots la capacité de s'adapter et d'évoluer. Les robots modernes, alimentés par des logiciels et du matériel de pointe, ont dépassé les tâches rigides pour apprendre et collaborer avec les humains, poussant l'efficacité et la productivité à des niveaux autrefois confinés à la science-fiction.
De la statique à la dynamique
L'époque où les robots exécutaient des routines programmées et monotones est révolue. En revanche, les robots modernes sont flexibles, capables d'effectuer plusieurs tâches à la fois et de s'adapter à l'évolution des besoins de l'industrie manufacturière. Prenons, par exemple, le système Robin d'Amazon, qui démontrée La société Amazon a déjà démontré sa capacité dynamique en triant plus d'un milliard de paquets en 2022. Amazon ayant déployé plus de 750 000 robots dans le monde, il ne s'agit pas seulement de quantité ; l'accent est désormais mis sur la polyvalence de ces machines, qui améliore l'utilisation des ressources et la rentabilité des opérations industrielles.Sécurité et renforcement des capacités humaines avec les cobots
L'intégration de la robotique dans la main-d'œuvre manufacturière est entrée dans une nouvelle phase avec l'avènement des "robots collaboratifs" ou "cobots". Ces machines sont conçues pour travailler aux côtés des humains, en améliorant la sécurité et en renforçant les capacités humaines. Cette collaboration crée un lieu de travail où la précision mécanique rencontre et amplifie l'ingéniosité humaine, favorisant un environnement de production plus productif et harmonieux.
Drones : la nouvelle ère de la technologie aérienne
Les drones ajoutent une autre perspective à ce paysage, ils ne sont plus seulement des outils pour la photographie aérienne ou des appareils de loisirs. Les drones remodèlent les processus de fabrication. Ils peuvent déplacer rapidement des marchandises dans de grands entrepôts, surveiller de vastes zones de production ou même contribuer à la gestion des stocks en scannant les produits depuis le ciel. Leur capacité à atteindre des endroits qui prennent du temps ou qui sont dangereux pour les humains en fait des atouts inestimables. Par exemple, les drones peuvent inspecter de grandes machines extérieures ou des composants d'infrastructure, en s'assurant de leur santé et de leur état de fonctionnement sans mettre en danger les travailleurs humains.
Apprentissage adaptatif et perception sensorielle
Les robots d'aujourd'hui sont équipés d'algorithmes d'apprentissage automatique, ce qui leur permet d'ajuster et d'améliorer leurs opérations en permanence. Associés à une perception sensorielle avancée, les robots peuvent détecter et interpréter les subtilités de leur environnement, ce qui leur permet de s'adapter en temps réel. Ce niveau de réactivité garantit que les tâches de fabrication sont exécutées avec un maximum de précision et d'efficacité, ce qui représente un progrès considérable par rapport aux robots statiques et dépendants des programmes du passé.
Cloud informatique
Cloud L'informatique est devenue un outil indispensable dans la vie de tous les jours. logiciel de fabrication numériqueIl permet non seulement d'optimiser les opérations, mais aussi d'assurer une collaboration mondiale transparente. Il transcende le simple stockage de données pour permettre un accès complet aux données, leur analyse et leur utilisation en temps réel. Cela permet de prendre des décisions plus intelligentes, d'optimiser les processus et de créer des modèles commerciaux innovants. Face à la complexité croissante des opérations mondiales et aux attentes grandissantes des clients, l'informatique dématérialisée s'impose comme une solution robuste offrant évolutivité, flexibilité et réponses inventives à ces défis modernes.
Une évolutivité sans précédent
Prenons l'exemple d'une entreprise manufacturière en démarrage qui connaît soudainement une augmentation massive de la demande. L'infrastructure informatique traditionnelle pourrait s'effondrer sous la pression, mais grâce à l'informatique en nuage, les fabricants peuvent passer à l'échelle supérieure en toute transparence. logiciel de fabrication numérique sans investissements initiaux importants. Cette élasticité signifie également qu'en période de ralentissement, les fabricants peuvent réduire les ressources, tout en maintenant la rentabilité. Cette évolutivité permet aux entreprises de s'adapter rapidement aux changements du marché, sans le décalage habituel des ajustements de l'infrastructure physique.
Analyses et informations en temps réel
Pour les secteurs disposant d'ensembles de données complexes, tels que la construction automobile, le traitement des données en temps réel dans le nuage change la donne. Il facilite les ajustements rapides en réponse aux défis logistiques, tels que les retards de livraison de pièces, en permettant de recalibrer immédiatement le calendrier de production. L'informatique en nuage relie également les équipes mondiales, leur donnant un accès instantané aux éléments suivants logiciel de fabrication numérique données et applications, ce qui permet d'harmoniser les flux de travail et d'accélérer le processus de prise de décision.
Amélioration de la collaboration
Les fournisseurs, les distributeurs et les unités de production étant souvent dispersés dans le monde entier, une communication efficace est vitale. Les plates-formes Cloud permettent à des équipes situées dans des zones géographiques différentes d'accéder aux mêmes informations. logiciel de fabrication numérique et des applications, ce qui permet de rationaliser la prise de décision. Par exemple, une équipe de conception en Allemagne peut instantanément partager des prototypes avec une unité de production en Chine, garantissant ainsi une production précise et rapide.
Sécurité et conformité
La sécurité est un autre pilier de l'informatique en nuage, les principaux fournisseurs proposant des mesures de sécurité avancées qui dépassent les capacités de chaque entreprise. Cette protection solide est essentielle pour se conformer aux réglementations régionales et internationales strictes, en particulier dans les secteurs très réglementés comme l'industrie pharmaceutique. Les services Cloud fournissent des pistes d'audit complètes, des outils de cryptage et de conformité, afin de protéger les données sensibles et de maintenir le respect des réglementations.
Innovation et évolution des modèles d'entreprise
Le cloud n'est pas seulement un outil opérationnel, c'est un tremplin pour l'innovation. En exploitant les algorithmes AI et ML alimentés par le cloud, les fabricants peuvent puiser dans une mine d'informations pour le développement et l'amélioration des produits. Il ouvre également la voie à de nouveaux modèles commerciaux, tels que le "logiciel en tant que service" (SaaS), où les entreprises étendent leurs offres au-delà des produits physiques pour inclure des services numériques et des analyses, enrichissant ainsi leur proposition de valeur.General Electric illustre l'application pratique de l'informatique en nuage, ayant transformé ses opérations commerciales grâce à une meilleure gestion des données, une collaboration rationalisée et la fourniture de services en temps réel, qui contribuent tous à accélérer les cycles de développement et de lancement des produits. Cela démontre le potentiel de l'informatique dématérialisée non seulement pour soutenir, mais aussi pour propulser activement l'industrie manufacturière vers l'avant.Blockchain
Tout comme le cloud computing remodèle la gestion et l'analyse des données, l'intégration de la technologie blockchain apporte un potentiel de transformation similaire à divers aspects de la fabrication, offrant une transparence accrue dans les chaînes d'approvisionnement, une protection solide de la propriété intellectuelle, des processus de transaction rationalisés et la promesse d'un modèle de production décentralisé. Tout comme l'informatique en nuage a ouvert la voie à l'analyse en temps réel et à la collaboration mondiale, la blockchain est prête à offrir un nouveau niveau d'intégrité et de sécurité, préparant le terrain pour un avenir où logiciel de fabrication numérique sont plus efficaces, plus sûres et plus transparentes.
Des chaînes d'approvisionnement transparentes
Le parcours d'un produit, de la matière première au consommateur final, comporte de multiples étapes et il est difficile d'en assurer la transparence. La blockchain enregistre chaque transaction ou changement chronologiquement et ne peut être modifiée rétroactivement. Prenons l'exemple de l'industrie du diamant : la technologie blockchain est désormais utilisée pour retracer le parcours de chaque diamant, garantissant ainsi qu'il provient d'une source éthique et qu'il est authentique. Les consommateurs et les parties prenantes bénéficient ainsi d'une confiance inégalée quant à l'origine et au parcours du produit.Au-delà de l'industrie du diamant, des acteurs majeurs tels que Honda et Ford ont pris des mesures innovantes en élaborant des projets de normes pour la blockchain. "passeports à pile"Ce passeport permettra de suivre l'empreinte environnementale et sociale des batteries automobiles. Ces passeports détailleront la chaîne d'approvisionnement d'une batterie, y compris l'origine des matériaux, les pourcentages de composants recyclés, les émissions de CO2 et les considérations relatives aux droits de l'homme.Protéger la propriété intellectuelle
Dans la lutte contre les produits contrefaits, la technologie blockchain apparaît comme une arme puissante pour les fabricants de divers secteurs. En enregistrant les détails de la conception, les spécifications et d'autres données connexes sur un grand livre décentralisé, les fabricants peuvent authentifier les produits authentiques. Par exemple, les marques de luxe pourraient intégrer les données de la blockchain dans leurs produits, ce qui permettrait aux acheteurs de vérifier leur authenticité, réduisant ainsi l'impact des produits contrefaits.
Rationalisation des paiements et des contrats
Les transactions financières traditionnelles, en particulier celles qui traversent les frontières internationales, sont souvent entachées de retards et d'erreurs. Les contrats intelligents de la blockchain sont conçus pour contourner ces difficultés, en automatisant les transactions, ce qui, à son tour, améliore l'efficacité et la précision. Si l'on prend l'exemple d'un fournisseur de pièces automobiles, un contrat intelligent peut être établi pour exécuter automatiquement le paiement dès la livraison et la vérification des marchandises, ce qui accélère le processus de transaction et minimise la probabilité de litiges.
Réseaux de fabrication décentralisés
En outre, la blockchain est la clé de la fabrication décentralisée, un concept qui devrait révolutionner la manière dont les produits sont fabriqués et le lieu où ils le sont. Dans ce futur envisagé, les unités de production individuelles, y compris les imprimantes 3D à domicile, pourraient être connectées par l'intermédiaire d'un réseau complet basé sur la blockchain. Les concepteurs pourraient ainsi transmettre les ordres de production à l'unité la plus proche capable de fabriquer l'article, ce qui améliorerait considérablement la vitesse de production et de livraison. Une telle évolution vers la décentralisation, soutenue par la transparence et la sécurité inhérentes à la blockchain, a le potentiel de modifier considérablement le paysage de la production, en le rendant plus dynamique et plus réactif aux demandes du marché.
Sécurité et fiabilité accrues des données
Dans le contexte de la fabrication, où les données sensibles sont l'élément vital de l'opération - qu'il s'agisse de dessins exclusifs ou d'informations sur les clients - la sécurité est de la plus haute importance. Face à la multiplication des violations de données, la blockchain se présente comme une formidable ligne de défense. Chaque entrée dans la blockchain nécessite un consensus, ce qui renforce l'intégrité et la fiabilité des données. Cet attribut garantit que les informations vitales restent protégées contre les cybermenaces, offrant ainsi une tranquillité d'esprit aux fabricants et à leurs clients.
Chacun de ces éléments - protection contre les contrefaçons, rationalisation des transactions avec des contrats intelligents, décentralisation des réseaux de fabrication et renforcement de la sécurité et de la fiabilité des données - démontre comment la blockchain peut créer un écosystème plus interconnecté et plus cohérent. Grâce à la blockchain, l'industrie peut parvenir à un processus de production sécurisé, efficace et fiable, reflétant la connectivité et l'intégrité globales que la technologie promet.
Réalité virtuelle et augmentée
Enfin, les technologies de réalité virtuelle et augmentée (RV et RA) sont passées du statut d'outils de jeu de pointe à celui d'atouts indispensables dans le paysage industriel. Grâce à leur capacité à créer des environnements numériques immersifs et à superposer des informations numériques au monde réel, ces technologies redéfinissent la manière dont les fabricants conçoivent, testent, produisent et même forment leur main-d'œuvre.
Conception de produits et prototypage
Dans le domaine de la conception et du prototypage de produits, où les méthodes traditionnelles peuvent être laborieuses et coûteuses, la RV et la RA représentent un bond en avant transformateur. Elles permettent aux concepteurs de visualiser les produits et d'y apporter des modifications dans un environnement virtuel en 3D, ce qui rationalise le processus de conception et réduit le besoin de modèles physiques. Les ingénieurs automobiles, par exemple, peuvent habiter virtuellement l'intérieur d'une voiture et en modifier la conception en temps réel - une efficacité qui s'apparente aux processus rationalisés rendus possibles par les contrats intelligents de la blockchain.
Assistance à l'entretien et à la réparation
La RA est particulièrement transformatrice dans les opérations de maintenance et de réparation, offrant un guide pratique et interactif aux techniciens. Les lunettes de RA peuvent projeter des données en temps réel et des instructions de réparation étape par étape sur les machines elles-mêmes, un peu comme la technologie blockchain améliore la transparence dans la production. Un technicien aéronautique, équipé de la RA, peut recevoir des informations superposées sur le moteur qu'il inspecte, ce qui garantit la précision et réduit les erreurs.
Formation et développement des compétences
La formation et le perfectionnement, essentiels au maintien d'une main-d'œuvre compétente, sont des domaines dans lesquels la RV offre des avantages incomparables. La RV offre un environnement sans risque. Les nouvelles recrues peuvent naviguer dans une usine virtuelle, interagir avec les machines et s'entraîner aux procédures, le tout sans les risques associés à la formation dans le monde réel. De même, la réalité augmentée peut fournir une formation sur le tas, où les travailleurs reçoivent un retour d'information et des instructions en temps réel lorsqu'ils exécutent des tâches.Par exemple, Rolls-Royce a exploité la puissance de la réalité virtuelle dans ses programmes de formation pour l'aviation d'affaires. Elle propose une formation à distance en RV qui se penche sur le moteur Rolls-Royce BR725, un moteur puissant pour l'avion d'affaires Gulfstream G650. Ce cours intensif de deux jours permet aux participants d'acquérir les compétences nécessaires à l'entretien et à la maintenance exceptionnelle du moteur. Andy Robinson de Rolls-Royce a souligné le rôle central de la numérisation dans leurs opérations et a décrit l'outil de RV comme un "changement de jeu" pour la formation technique. Bien que la formation par RV ne remplace pas l'expérience pratique, elle offre des avantages distincts, tels que l'élimination du besoin d'un moteur de formation grandeur nature et la fourniture de scénarios interactifs réalistes sous la direction d'un instructeur. Cette approche innovante garantit que la formation dans l'industrie manufacturière reste efficace, efficiente et sûre.Collaboration à distance
À une époque où la collaboration mondiale est la norme, la RV et la RA comblent les distances en permettant à des équipes du monde entier de travailler ensemble dans un espace virtuel partagé, ce qui fait écho aux possibilités de collaboration offertes par l'informatique en nuage. Les concepteurs et les techniciens peuvent interagir avec un produit ou effectuer des opérations de réparation à l'unisson, même s'ils sont séparés par des continents. Cette capacité est particulièrement cruciale pour minimiser l'impact des restrictions de voyage et la nécessité d'une présence physique, en favorisant un flux de travail continu et sans faille.
Par essence, les technologies de RV et de RA ne sont pas des merveilles autonomes ; elles s'intègrent profondément à d'autres innovations numériques pour créer un paysage manufacturier cohérent et à la pointe du progrès. Elles s'alignent sur les évolutions fondamentales vers une connectivité accrue, une collaboration en temps réel et une efficacité renforcée qui caractérisent les processus de production contemporains, sous l'impulsion de transformation numérique de l'industrie manufacturière.
L'impératif d'intégration
Les fabricants prospères de demain seront probablement ceux qui comprennent que ces technologies ne sont pas des pièces isolées, mais des éléments d'un puzzle plus vaste. L'intégration est la clé - le mélange harmonieux de AI, ML, blockchain, VR et AR est ce qui conduira à une nouvelle ère de l'automatisation des usines, marquée par des solutions plus intelligentes et des opérations plus résilientes. Entreprises de fabrication numérique sont à l'avant-garde de cette intégration et sont les pionniers de la fusion de ces technologies pour redéfinir le paysage de la production industrielle.
En conclusion, la révolution numérique dans l'industrie manufacturière ne consiste pas seulement à adopter de nouvelles technologies, mais aussi à les intégrer dans le tissu des opérations industrielles afin de créer un environnement de production plus connecté, plus intelligent et plus adaptable. Alors que les frontières entre les mondes physique et numérique continuent de s'estomper, la révolution numérique dans l'industrie manufacturière n'est pas seulement une question d'adoption de nouvelles technologies. entreprises de fabrication numérique sont à l'aube d'une nouvelle renaissance industrielle, sous l'impulsion de la numérisation.
FAQ
Solutions de fabrication numérique englobent un ensemble de technologies avancées qui intègrent les processus de production numériques et physiques. Ces solutions comprennent la conception assistée par ordinateur (CAO), la fabrication assistée par ordinateur (FAO), l'impression 3D, la robotique, l'intelligence artificielle et l'internet des objets (IoT). Elles permettent aux fabricants de créer un jumeau numérique du processus de fabrication, ce qui permet de simuler, d'optimiser et de contrôler la chaîne de production dans un environnement virtuel avant le début de la production physique. Cette approche améliore l'efficacité, la flexibilité et les délais de mise sur le marché tout en réduisant les coûts et en permettant une personnalisation de masse. En exploitant les données et les analyses en temps réel, les solutions de fabrication numérique facilitent la maintenance prédictive, l'amélioration de la gestion de la chaîne d'approvisionnement et une meilleure prise de décision en général, ce qui conduit à des opérations de fabrication plus intelligentes, plus souples et plus durables. Entreprises de fabrication numérique tirer parti de ces solutions pour repousser les limites du possible dans le domaine de la fabrication.
La transformation numérique dans la fabrication rationalise les opérations en intégrant des technologies avancées telles que le AI, l'IoT et la robotique, ce qui se traduit par une efficacité accrue et une réduction des coûts opérationnels. Elle permet une maintenance prédictive, minimisant les temps d'arrêt, et permet une plus grande évolutivité et flexibilité dans la production. L'analyse des données en temps réel issue de la transformation numérique aide les fabricants à prendre des décisions éclairées, à optimiser les chaînes d'approvisionnement et à répondre rapidement aux évolutions du marché. En fin de compte, elle améliore la qualité des produits, la satisfaction des clients et favorise l'innovation, ce qui permet aux fabricants de rester compétitifs dans un paysage industriel qui évolue rapidement.
La fabrication numérique est en effet adaptée aux petites entreprises, car elle leur offre l'évolutivité, la flexibilité et l'efficacité qui leur permettent de rivaliser avec leurs concurrents plus importants. En adoptant des technologies telles que l'impression 3D, les petites entreprises peuvent produire de petits lots de manière rentable, personnaliser leurs produits et réaliser rapidement des prototypes. Les outils numériques permettent également de rationaliser les opérations, de réduire les déchets et d'améliorer le contrôle de la qualité avec plus de précision. Si l'investissement initial et la courbe d'apprentissage peuvent poser problème, les avantages à long terme liés à l'amélioration de la productivité et à la capacité de s'adapter rapidement à l'évolution du marché peuvent être considérables, faisant de la fabrication numérique une option viable et stratégique pour les petites entreprises désireuses d'innover et de se développer. Entreprises de fabrication numérique offrent souvent des solutions évolutives qui conviennent aux entreprises de toutes tailles, y compris les petites entreprises.
La fabrication numérique joue un rôle essentiel dans la promotion de la durabilité et la prise en compte des préoccupations environnementales en permettant une utilisation plus efficace des ressources et en réduisant les déchets grâce à des techniques de production précises telles que la fabrication additive (impression 3D). Elle facilite l'optimisation des chaînes d'approvisionnement, en réduisant l'empreinte carbone associée à la logistique. En tirant parti de l'analyse des données et de l'IdO, la fabrication numérique peut également améliorer l'efficacité énergétique au sein des installations de production et permettre le recyclage des matériaux. En outre, elle soutient la création de produits durables grâce à l'analyse du cycle de vie et à l'utilisation de matériaux écologiques dans le processus de conception, contribuant finalement à une industrie manufacturière plus durable avec un impact environnemental réduit. Entreprises de fabrication numérique offrent souvent des solutions évolutives qui conviennent aux entreprises de toutes tailles, y compris les petites entreprises.
Adopter solutions de fabrication numérique présente plusieurs défis, notamment un investissement initial important dans la technologie et la formation, ce qui peut être particulièrement décourageant pour les petites et moyennes entreprises. Il est également nécessaire d'opérer un changement culturel au sein des organisations afin d'adopter l'innovation et l'apprentissage continus. L'intégration de nouveaux systèmes numériques dans l'infrastructure informatique existante pose souvent des difficultés techniques, et il devient plus complexe de garantir la sécurité des données dans un environnement de plus en plus interconnecté. En outre, il est de plus en plus difficile de trouver et de conserver des travailleurs qualifiés capables de naviguer dans les outils numériques avancés. Pour surmonter ces obstacles, il faut une planification minutieuse, une volonté d'investir dans le capital humain et une approche stratégique de l'intégration numérique.