Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.



Most businesses don’t need to be convinced that inefficiency is a problem. They see it every day. Staff are wasting hours on data entry. Critical processes depend on copy-paste workarounds. Systems that don’t sync, and teams compensating for it manually. It’s not a one-off issue. It’s structural.
Robotic process automation (RPA) offers a practical way to fix repeatable workflows in all kinds of domains, including finance, HR, supply chain, claims, and customer ops. You define the logic, connect the systems, and let software do its thing.
According to Deloitte’s Intelligent Automation report from 2022, 74% of organizations had already adopted RPA, and more than half were scaling it across departments (up from just 13% five years earlier). Even back then, it was already well into rollout mode.
And it hasn’t slowed down. The RPA market was worth just over $3 billion in 2023, and it’s on track to hit $13 billion by 2030. Which checks out: you don’t get that kind of growth unless people are seeing actual returns, not just buying licenses.
The gap between “we tried RPA” and “RPA transformed our business” usually comes down to implementation. This guide maps out when to use RPA (by industry and by function) so you can get it right from the start and see the ROI.
RPA is simple in theory: software bots mimic the way a human interacts with digital systems. They click buttons, copy data, fill out forms, send emails, pull records — anything that follows a predictable pattern. What makes it powerful is scale. These bots can work 24/7, across platforms, with zero drop in speed or accuracy.
What sets RPA apart from traditional automation is that it doesn’t need deep system integration or API-level access. It can work on top of existing systems (web apps, desktop tools, ERPs, CRMs) by interacting with the interface, just like a human would. That’s a big reason why so many companies adopt RPA first before diving into more complex digital transformation projects.
“RPA lets us get results without waiting on major system changes. If two platforms don’t integrate, that’s fine: the bot bridges the gap. It’s often the fastest way to fix broken processes without touching the core tech stack.”

CTO at Innowise
Now, not every task is a good fit for automation. Some processes look like good candidates at first. Until you realize they’re full of edge cases, require human judgment, or change too often to be worth maintaining. Over the years, I’ve learned to spot the patterns of a solid robotic process automation use case. Here’s what to look for:
If someone’s doing the same clicks and keystrokes hundreds of times a week, a bot can probably do it faster and more reliably. Think invoice data entry, claims validation, or copying data between systems.
RPA doesn’t think, but follows instructions. The ideal process has well-documented rules and decision points (e.g., “If field A is X, then send it to team B”). If the workflow involves gut instinct or nuanced reasoning, it’s probably not a fit.
Processes with too many edge cases tend to break down in automation. If 90% of your tasks follow the same pattern and the remaining 10% require human handling, that’s workable. If every third case needs a manual override, you’re better off optimizing the process first.
One of the best robotic process automation use cases is stitching together systems that don’t natively integrate. Bots can log into your CRM, pull customer details, feed that data into your ERP, and email a confirmation. No dev time required.
If the process changes every month, maintaining the bot becomes a full-time job. The most ROI comes from automating mature, predictable workflows where the steps are unlikely to shift overnight.
There’s a reason RPA is catching on across entire sectors: the problems it solves aren’t unique to any one industry. Repetitive tasks, disconnected systems, inconsistent data, and costly manual workarounds show up everywhere, from hospitals to warehouses to call centers. What changes is the context.
Below is a breakdown of how RPA is being used across different industries. For some, we’ve gone deeper in dedicated posts (linked where available) with real examples and implementation insights.
| Industry | High-value RPA use cases |
| Retail & distribution | Purchase order processing, inventory reconciliation, shipment tracking, supplier onboarding |
| Healthcare | Claims processing, patient intake, appointment scheduling, insurance verification |
| Banking & finance | KYC checks, loan processing, reconciliation, regulatory reporting |
| Logistics | Route scheduling, freight billing, customs documentation, carrier onboarding |
| Manufacturing | Production order management, BOM updates, compliance checks, supplier communications |
| Insurance | Claims validation, policy updates, quote generation, regulatory submissions |
| Telecom | Customer onboarding, billing updates, SIM swaps, plan changes |
| Automotive | Warranty claims, VIN registration, compliance tracking, supplier data updates |
Supply chain management thrives on timing and accuracy. But when you’re dealing with multiple vendors, fluctuating inventory, and region-specific logistics, things get messy fast. That’s where RPA proves its worth by tightening the handoffs between systems and flagging exceptions before they snowball.
For example, bots can monitor stock levels in real-time and automatically trigger reorders when set thresholds are reached. They can validate vendor invoices against delivery records, match POs, and update ERP entries without manual intervention. When integrated with shipment tracking systems, RPA can generate status updates and send alerts for delays or discrepancies. As a result, you get fewer stockouts, faster procurement cycles, and tighter control over fulfillment workflows.
In healthcare, administrative overhead often gets in the way of actual care delivery. Staff spend hours re-entering data between systems, chasing paperwork, and verifying insurance — all while under pressure to reduce errors and stay compliant.
RPA offers a way to automate those routine, rules-based interactions. Bots can handle patient intake forms, validate insurance details in real time, schedule appointments based on provider availability, and flag billing errors before claims are submitted.
On the clinical side, RPA can support lab result entry, document routing, and audit trail generation. It works alongside EHR systems to reduce friction and free up staff for higher-value work.
Banks and financial institutions face a unique double bind: they need to scale operations while staying airtight on compliance. Most back-office teams are still drowning in paper-heavy workflows: loan processing, customer onboarding, risk checks, and reconciliations.
RPA helps by standardizing and accelerating these workflows. Bots can auto-populate forms for KYC, run background checks against sanction lists, and compile data from multiple systems into a single onboarding report. On the finance side, bots can reconcile thousands of transactions across accounts, flag mismatches, and generate exception reports. And all that with detailed audit logs. They can even help with regulatory submissions by compiling data and filling out forms in the right format. The result is a faster, cleaner back office that handles more work without needing more hires.
For logistics providers, speed and transparency are everything. But most are held back by disconnected tools: one for fleet management, another for tracking, a third for billing. Every manual update creates a delay and a risk of error.
With RPA, these gaps can be bridged automatically. Bots can fetch real-time tracking data from carrier portals, update shipment statuses in customer-facing systems, and trigger alerts if deliveries fall outside SLA windows. Internally, they can handle load planning, customs documentation, and even driver onboarding by pulling credentials from government databases and populating TMS or HR systems. That makes the whole system more predictable.
Manufacturing operations often involve complex, layered workflows where one delay upstream can disrupt everything downstream. Much of this fragility comes from manual process dependencies: scheduling, documentation, supplier coordination, and data transfer between MES, ERP, and QA systems.
We helped a client in the manufacturing sector automate core workflows tied to production order management and supplier communication. We built and deployed a set of RPA bots using UiPath to automate procurement from end to end. Bots now extract order data from emails (including printed or handwritten text via OCR), validate pricing and quantity, and enter everything into the order system automatically. Another set of bots processes invoices, compares them against POs, and either approves them or routes them for review. We also automated real-time shipment tracking and integrated those updates directly into their CRM.
Their procurement processes are now 27% faster, inventory records are more accurate, and the team has freed up the capacity equal to 6 full-time equivalents (FTEs) — all without touching their existing ERP stack.
Insurance companies process thousands of claims, policies, and customer service requests daily. Every one of those interactions typically requires accessing multiple systems, verifying data, and generating documentation, all ripe for automation.
In our work with a major insurance client, we developed an RPA solution with OCR and ML capabilities to automate claims intake, pull data from police reports and medical records, and flag missing or suspicious information in real time. On the underwriting side, bots gathered risk data, cross-referenced it with historical claims, and supported more accurate pricing. That boosted underwriting precision by 34%.
We also automated settlement processing and compliance checks, enabling the system to flag policy violations, verify KYC data, and freeze transactions when limits were exceeded. Altogether, this brought a 27% reduction in claim registration time and helped the insurer reduce errors, fraud risk, and audit exposure, maintaining full regulatory traceability.
Telecom providers run some of the most operationally complex businesses out there, with millions of accounts, high churn rates, and strict SLA commitments. The front line is customer service, but behind that lies a tangled web of billing, service provisioning, and technical support.
RPA plays a big role in smoothing out that complexity. Bots can handle service activations, automate number porting between carriers, and push billing updates across CRM and ERP systems. On the support side, bots can read inbound email queries, classify them based on intent, and generate first-level responses or route the ticket directly with all necessary context attached. This reduces queue times, improves consistency, and takes pressure off human agents handling more complex issues.
The automotive industry deals with global supply chains, strict compliance rules, and an ever-evolving product lifecycle, all of which depend on detailed, accurate documentation. Add to that the rise of connected vehicles and aftermarket services, and the need for back-office efficiency becomes even more critical.
RPA helps by stitching together production, logistics, warranty, and dealer support workflows. Bots can manage supplier scorecards, verify part certifications, trigger warranty eligibility checks, and process return authorizations.
On the retail side, bots can register vehicles with the DMV on the buyer’s behalf and handle rebate processing. They create a smoother, more resilient operational model across the board.
Now let’s zoom in on the actual tasks being automated. These are the kinds of workflows that show up everywhere, whether you’re in banking, logistics, healthcare, or retail. Think of this as your functional use cases for RPA checklist: what RPA can realistically handle today, where it adds the most value, and what to watch out for during implementation.
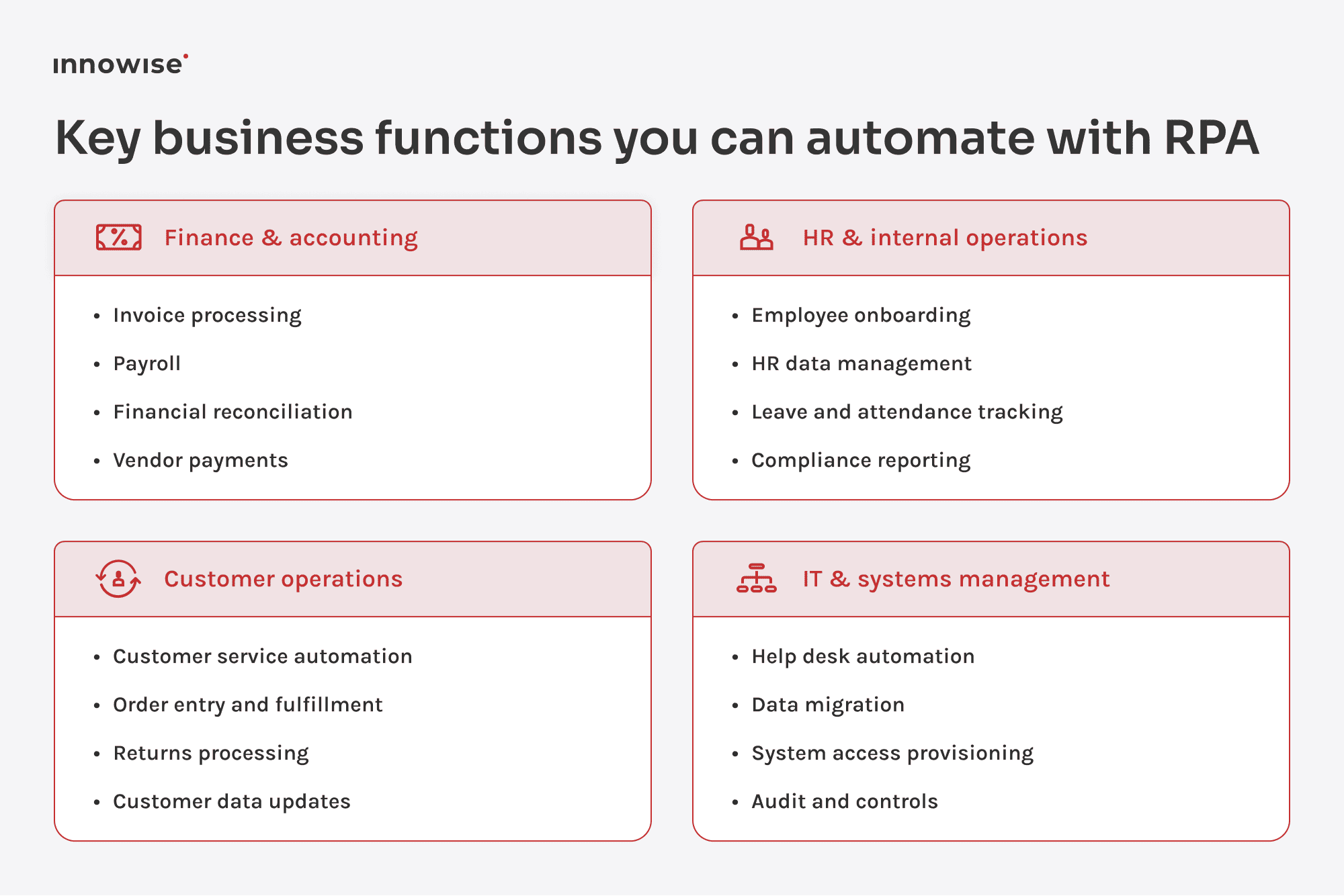
RPA is a great fit for AP workflows, especially when invoice formats are standardized. Bots can ingest invoices via email or shared folders, extract fields (vendor, PO number, line items), check for 3-way match, and push data into the accounting system.
Pro tip: Before jumping into automation, audit your invoice formats. If vendors are all over the place with layouts or languages, you may need to pair RPA with OCR or intelligent document processing (IDP). And always map out exception handling. Not every invoice will match perfectly, and unresolved exceptions can quietly pile up if there’s no clear escalation path.
And start with automating only the “clean” invoices — the ones that don’t need human review. Then gradually expand. Don’t go all-in on day one.
Anytime a team is copying data from one system to another (CRM to ERP, spreadsheets to database, tool A to tool B), that’s an RPA opportunity. Bots excel at this kind of rule-driven, structured movement.
But here’s what people forget: data quality matters. Garbage in, garbage out: if your source data is inconsistent or full of hidden dependencies, the bot will replicate those flaws at scale. I’ve seen clients try to migrate legacy data with automation, only to realize halfway through that half the values were outdated or mislabeled.
Pro tip: Pair your RPA initiative with a lightweight data quality check. You don’t need a full MDM program. Even just flagging missing values or abnormal patterns will save headaches later.
RPA bots can make customer service teams faster and more consistent. A bot can scan incoming support emails, categorize them, attach relevant customer data, and either send a templated response or route the case to the right agent queue.
It shines when you’ve got repeatable scenarios: order status checks, billing questions, and account resets. Bots won’t solve edge cases, but they’ll clean up the bulk queue and reduce SLAs dramatically.
Pro tip: Avoid letting bots reply to complex or emotionally charged tickets. Rule of thumb: if a customer’s tone is angry, confused, or panicked, escalate to a human. Don’t burn goodwill on automation that feels robotic.
The same approach works for IT help desks. Most tickets are repetitive (password resets, software installs, permission changes), and bots can handle them instantly, freeing up the IT team for actual technical challenges. Integrated with ITSM platforms like Jira or ServiceNow, bots can check ticket details, resolve known issues, or escalate with context for a seamless hybrid support model.
Pro tip: Start with password resets and access provisioning as they’re low-risk, high-volume, and deliver instant ROI. Then branch out into more complex automations over time.
Order-to-cash involves a chain of dependent steps: order intake, verification, inventory allocation, invoicing, shipping, and sometimes returns. A missed step can mean a delayed shipment or even a missed sale.
RPA can help tie all these steps together across systems. Bots can validate orders, check SKUs, trigger fulfillment workflows, update the CRM, and notify customers, all without human involvement.
Pro tip: Watch out for edge-case logic. Discounts, bundles, or multi-region orders can get tricky if your rules aren’t airtight. I recommend mapping out the top 80% of order types and starting there. Build modular bots that you can plug new logic into later.
The onboarding experience sets the tone for the entire employee lifecycle. Yet in many companies, it’s still a mess of training docs, emails, and forgotten steps. RPA bots can set up accounts, assign training, request badge access, send welcome emails, and update HRIS records in real time.
Here’s something that works well: building a checklist-style workflow with clear “handoff” points between bots and HR. For example, the bot creates accounts and schedules the welcome session, but the manager approves some role-specific tools. This way, you’re giving HR space to focus on culture and engagement instead of chasing IT tickets.
Pro tip: Always audit your onboarding process before you automate. Most companies have gaps they’re not even aware of.
Regulatory reporting is a classic case of “low complexity, high consequence.” You’re gathering data from multiple systems, checking that it fits predefined formats, and submitting it on time. RPA is tailor-made for this: bots can extract the required fields, populate the right templates, double-check calculations, and submit reports on schedule.
Pro tip: Build in version control and clear audit trails. Regulators may request proof of how a report was generated, and your bot logs should be as transparent as any human record. Also, don’t forget about fallback protocols if your ERP goes down or if input data is late. What should the bot do?
What helps is tying your bots into change management processes. If a regulation changes, someone needs to update the automation logic. Assigning that ownership early makes all the difference.
Payroll has zero tolerance for errors. RPA helps by pulling timesheet data, calculating gross and net pay, applying deductions, generating payslips, and syncing with payment providers.
Pro tip: Use RPA to validate rather than own payroll end-to-end. For example, have the bot run a parallel calculation and flag discrepancies. This catches human input errors and protects against under/overpayments.
And always test bots during a non-critical cycle (e.g., mid-month dummy run) before pushing live on payday. A misstep in production can trigger payroll reprocessing, which is every HR team’s nightmare.
Procurement often involves fragmented workflows: request approvals, quote comparisons, vendor verification, PO creation, and delivery confirmations. Bots can close the loop between all these steps, ensuring speed and traceability.
What’s often overlooked is contract compliance. RPA bots can cross-check incoming invoices against negotiated terms (quantities, pricing, delivery windows) and flag discrepancies automatically. That’s huge for organizations trying to get control over tail spend.
Pro tip: Build in soft approvals. For example, let the bot prepare the PO, but send it to the procurement manager for one-click review. This keeps human judgment where needed, without slowing things down.
Marketing teams are often buried in repetitive operational work: scheduling posts, cleaning lists, sending nurture emails, and compiling reports. RPA can take care of all of that, and more, without touching the creative side.
Automation isn’t just for ops; it also enables smarter targeting. Bots can segment leads by behavior, update CRM fields based on actions, or trigger campaigns based on customer lifecycle stage.
Pro tip: If you’re running multi-channel campaigns, use RPA to centralize reporting. Pull metrics from Facebook, LinkedIn, Google Ads, and your email tool into a single dashboard. Saves hours of spreadsheet work every week.
Reconciliation is tedious but critical. You’re matching records from different systems (say, internal ledgers vs. bank statements) and investigating every mismatch. RPA handles this with surgical precision: comparing entries, applying rules, flagging exceptions, and generating reports.
But don’t try to automate every reconciliation scenario at once. Start with high-volume, rule-based accounts (e.g., daily cash receipts), then expand to more complex ones. Also, always log exceptions in a human-readable format. I’ve seen bots flag errors without enough context to debug, which defeats the point.
Pro tip: Set bots to run on a rolling basis (e.g., hourly or daily), not just at month-end. This spreads out the workload and makes the end-of-month closing much smoother.
Claims processing is document-heavy, rule-bound, and time-sensitive. In other words, ideal for RPA. Bots can extract data from forms, check claim eligibility, verify documentation, and route valid cases to assessors or auto-approve low-value ones.
Remember, the “first notice of loss” (FNOL) is key. If you can automate triage right at intake (checking for missing info, identifying claim type, pre-classifying severity), you dramatically reduce turnaround time.
Pro tip: Pair RPA with NLP if your claims forms have a lot of free text. Structured data is ideal, but smart parsing adds flexibility and scalability.
Sales teams generate orders through emails, web forms, or CRMs, and often someone in ops has to re-enter that into the ERP or OMS. Bots eliminate that bottleneck by scraping order data, validating SKUs, checking inventory, and pushing it into downstream systems.
Pro tip: Pay attention to how pricing rules are applied. Discounts, tiers, and bundled offers may need dynamic logic, not just field mapping. Validate that logic early.
And send a confirmation to the sales rep or customer once the bot processes the order. That builds trust in the automation and helps catch any edge-case issues fast.
Inventory accuracy is a moving target, especially across distributed warehouses. RPA can monitor stock levels, trigger reorders, update inventory ledgers, and sync data between procurement, finance, and warehouse systems.
What’s valuable is that bots can also validate that what was ordered is what was received. Matching packing slips to POs, flagging quantity mismatches — these small automations prevent big downstream problems.
Pro tip: Watch out for inventory systems that require manual confirmation or complex UOM (unit of measure) logic. In those cases, loop in a human for approvals until you’ve got a clean automation path.
Most companies have contracts sitting in shared drives or inboxes, with no reliable system for renewals, obligations, or clause visibility. RPA can extract metadata (e.g., production dates, payment terms), store documents in the right system, and trigger alerts for key dates.
Pro tip: Don’t try to parse entire contracts with RPA alone. Use it in tandem with a contract lifecycle management (CLM) system or OCR + NLP engine. The CLM handles structured storage, version control, and approval workflows, while NLP extracts clauses, terms, and key dates from unstructured text. RPA does the heavy lifting of moving files, applying logic, and keeping everything up to date.
Dirty data is the root cause of a lot of business pain, especially when customer info is spread across platforms. RPA helps keep records in sync by validating inputs, updating CRM entries, and propagating accurate, standardized records across integrated platforms.
Watch for source of truth issues. If your CRM and billing system both store customer names, which one wins when there’s a mismatch? Bots need clear rules, or they’ll just replicate inconsistency.
Pro tip: Use bots to regularly run deduplication logic or verify records against public databases (e.g., VAT validation, address lookups). Clean data = better decisions.
In healthcare, billing mistakes create delays, denials, and compliance risk. RPA can automate charge capture, insurance verification, claim submission, and denial tracking while logging every action for audit readiness.
A common pitfall here is mismatches in CPT codes or authorization numbers. Your bot needs to check billing rules at the payer level. What’s valid for one insurer might fail for another.
Pro tip: Set up alerts when claims are stuck in limbo. Bots can flag claims not paid within X days or missing required follow-up, so you don’t lose revenue waiting for resolution.
Payment cycles can easily break down, especially when invoice approvals, contract checks, and bank transfers span different teams. RPA can handle the end-to-end flow: invoice matching, payment validation, and disbursement via integrated banking APIs.
Pro tip: Introduce thresholds. For example, bots can auto-pay invoices under $500, while routing larger ones for finance approval. It balances speed with control.
And build exception dashboards, don’t just send email alerts. Seeing pending approvals, flagged invoices, or blocked payments in one view makes life easier for finance.
Returns involve a mix of logistics, finance, and CX, which are all tied together by case-specific rules. RPA can validate return requests, generate RMAs, update inventory counts, issue refunds, and notify the customer once processed.
Pro tip: Link your bot to your ecommerce platform or ticketing system. When a customer initiates a return, the bot can immediately start processing, which reduces turnaround time and improves satisfaction.
Note that you’ll need exception handling for damaged items, return policy violations, or incomplete returns. Those are best handled via a human queue, not automation.
Digitizing and categorizing documents isn’t glamorous work, but it’s necessary. RPA bots can scan folders, read document types, extract metadata, rename files, and route them into the right storage system or DMS. So, the best use case here is regulatory or legal documents that need to be consistently organized and easily searchable for audits.
Pro tip: Define a naming convention early. Bots follow instructions, so unclear logic is an express ticket to ClutterTown. Also, automate indexing so users can retrieve documents later by tag, not just file name.
Audit prep is usually a scramble of spreadsheets, system logs, and evidence requests. RPA streamlines this by collecting required records, checking them against predefined controls, and assembling audit-ready reports.
Pro tip: run bots on a schedule (e.g., weekly) rather than just at audit time. It keeps your internal controls tight all year round.
RPA can monitor feedback channels (email, NPS surveys, app stores) and route feedback by theme or urgency. Paired with NLP, it can detect sentiment, flag critical issues, and summarize trends over time.
Pro tip: Don’t stop at reporting. Feed these insights back into product or support workflows. If complaints about a feature spike, the bot can flag the trend, compile key details, and create a draft Jira ticket for the product manager to review.
Also, run scheduled snapshots. Weekly digest emails to customer success or product leads help keep the voice of the customer visible without manual effort.
Bots can monitor transactions, access logs, and configuration settings to spot deviations or policy violations. If something breaks a rule, the bot flags it, triggers alerts, and can even roll back changes in some cases.
Pro tip: Use bots to enforce policy proactively. For example, if someone tries to create a vendor without approval, the bot blocks it and alerts procurement.
Don’t forget that bots need compliance, too. Set up audit trails for your automation logic, especially in regulated industries.
If you’ve made it this far, chances are you’ve already seen the potential in the kind of day-to-day friction RPA can actually remove. Faster invoice approvals, cleaner handoffs between teams, fewer errors across systems, and hours of manual work saved — these all translate into more capacity for strategic work.
That’s what we focus on at Innowise. We’ve spent years designing, building, and scaling RPA solutions across industries from manufacturing and logistics to finance, healthcare, and beyond. Whether you need to automate a single process or lay the groundwork for enterprise-wide transformation, we don’t come in with buzzwords. We come in with a clear understanding of what works, what breaks, and what moves the needle.
And we don’t just build bots. We build systems with the exception handling, documentation, and governance you’ll wish you’d had from day one.
If you’re ready to move past the inefficiencies, we’re ready to help you get there.

Director, Head of Java, ERP solutions
Michael knows ERP inside and out — from choosing the right system to figuring out how it’ll work with the rest of your tech stack. He’s the one people turn to when they need ERP to solve real operational problems, not create new ones.












Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.