Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.


Extended reality refers to a suite of cutting-edge technologies enabling individuals to expand, enhance, or completely transform their perception of reality, embracing unseen experiences and interactions. While virtual reality creates a fully simulated, computer-generated environment mainly through headsets, augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical world through phones and tablets, and mixed reality blends the two seamlessly, they are bringing about a new era of perception and communication.
From healthcare and retail to education and entertainment, XR is rapidly becoming a game-changer across multiple industries, with the market value projected to reach an impressive $300 billion by 2024.
The history of virtual reality for business can be traced back to the development of the Sword of Damocles head-mounted display system by Ivan Sutherland in 1968 or the work of Jaron Lanier at VPL Research in the mid-1980s for those unfamiliar with computer science. On the contrary, augmented reality technology has a longer history, going back to the military’s development of heads-up displays in the 1950s. However, even though these technologies have been around for decades, their widespread adoption has been limited, only recently demonstrating astounding capabilities in addressing issues and simplifying daily life.
Today, building high-resolution lightweight XR devices has become more affordable with modern advancements in hardware technologies. Furthermore, enhanced user experiences have significantly increased interest in XR technologies, especially for entertainment, education, and training purposes. IT evangelists and XR amateurs worldwide predict that more technological breakdowns are ahead due to hardware improvements, solid investments, and a growing number of XR use cases.

Nine extended reality examples
Through virtual training simulations and unmatched remote experiences, XR connects people and spaces worldwide, staying relevant in today’s highly volatile economy. Utilizing XR technology today reveals new boundaries, resulting in significant social impact across healthcare, education, e-commerce, and many other sectors.
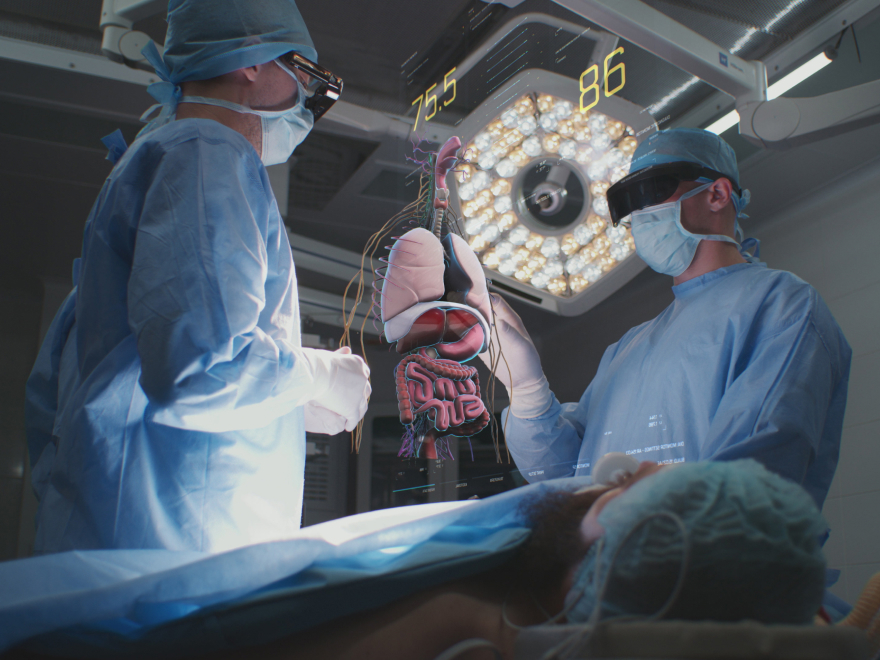
VR technology can benefit healthcare in numerous ways, including mental health, professional education, pharmaceutical development, etc. In addition, it facilitates collaboration between different medical departments during a pandemic when remote care has become increasingly vital.
Extended reality has revolutionized medical imaging, such as MRI and CT scans, allowing clinicians to practice skills and meticulously prepare for complex operations in a risk-free environment. As a result, AR helps medical staff make informed decisions during live surgeries or patient care and provides insightful recommendations, allowing people to overcome their fears in a safe and controlled environment.
Compared to lectures and readings, VR has a retention rate of 75%, making learning more engaging and effective than watching videos or reading books, according to the National Education Association. In addition, augmented reality offers students hands-on experiences in real-world scenarios without the need for a physical classroom, allowing learners to engage in practicing surgery or exploring outer space.
With XR, you can take virtual field trips to physically impossible places or explore complex scientific concepts in more detail, such as a 3D molecule model. Through all-around immersion, XR technology is particularly beneficial for remote learning at the post-secondary level, enhancing comprehension of various topics, from biology to astronomy.

As the business world continues to accelerate, having a skilled workforce has become more critical than ever, with XR tools saving time and money. Engineers and manufacturers frequently perform hazardous functions, so VR can help them complete full-fledged training in a safe, risk-free environment before they begin working. This way, simulations can also assist in training new factory employees to use risky equipment properly, regardless of location, tight deadlines, distractions, or other pressing factors.
Furthermore, employees can obtain visual or voice instructions and view data on smartphones, headsets, or other digital devices, driving productivity along critical stages of the production process.
Augmented reality has emerged as a game-changer in the retail industry, enhancing both online and offline shopping experiences. Thus, in brick-and-mortar stores, XR can be used to create immersive product visualization experiences, allowing customers to interact with 3D products in a digital space or help them find products and navigate stores more easily. This improves product understanding, increases engagement, and reduces purchase hesitation.
For e-commerce, AR can help shoppers enjoy an in-person experience from the comfort of their homes, enabling humans to interact with a product before making a purchase. Furthermore, augmented reality in business eliminates expensive return problems by allowing customers to virtually try a product before acquiring it. Particularly, the “try before you buy” AR-powered visualization by Macy’s has aided the company in diminishing its return rates to less than 2%.
The food industry is multifaceted, with XR technology offering innovative solutions such as virtual food production and simulated scenarios to amaze customers. For instance, restaurants are now using XR technology by offering placemats that double as recipe books or gaming platforms, engaging visitors once they place an order.
In the food & beverage industry, XR is often used to ensure proper hygiene in food facilities. Unlike human error-prone and oversight-lacking manual inspection routines, MR devices highlight critical areas and ensure they are inspected thoroughly. Additionally, these devices have a no-oversight feature that prevents workers from moving on until all necessary steps have been completed. Moreover, food operators can capture and store content in a database, enhancing the traceability of hygiene inspections.
By 2023, the XR entertainment and gaming market is predicted to strike $18 billion, making it the largest segment in the industry. Virtual reality headsets allow gamers to immerse themselves in digital environments, including historical settings, otherworldly realms, live concerts, and sports battles. Numerous game developers are now releasing their own virtual reality headsets to meet the demand of their audiences. Given the gaming industry’s highly competitive nature, VR-enabled devices will continue to advance in a truly innovative way.

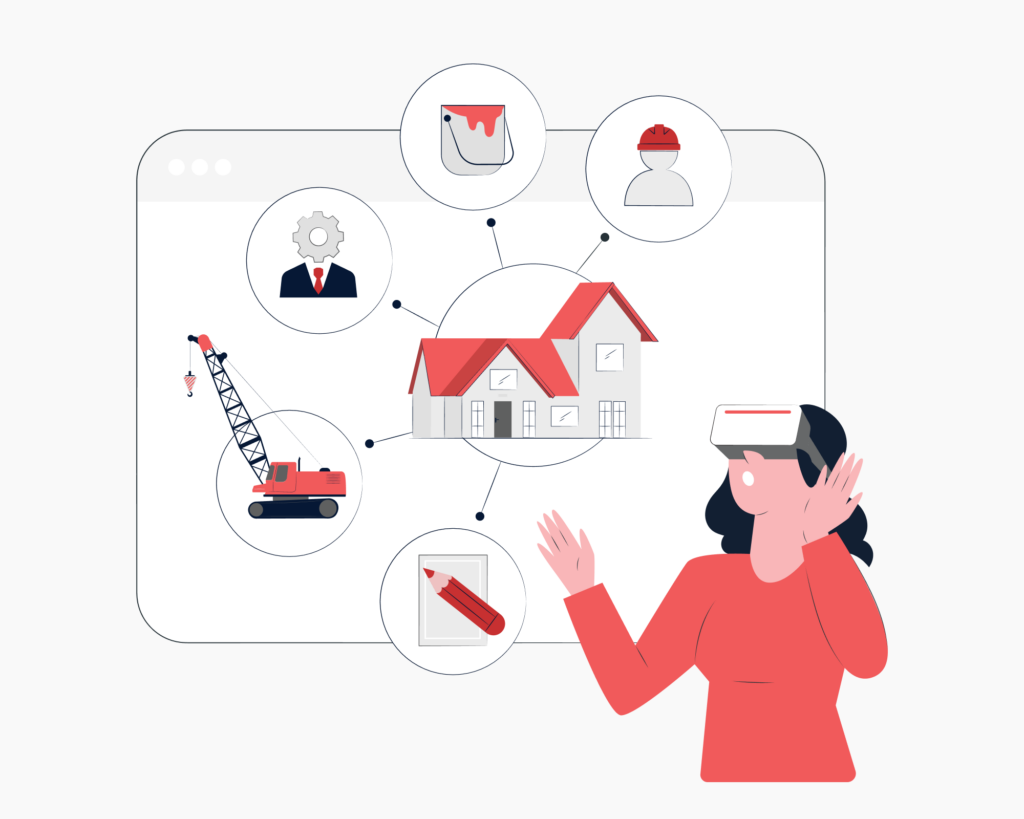
With modern XR and smartphones, real estate agents can showcase properties to potential buyers remotely, as if they were physically present, regardless of location. They can create advertisements, sales pitches, and virtual open houses that can be accessed through smartphones or headsets. Some web browsers already have built-in tools that allow real estate agents to take advantage of XR’s fundamental features.
Augmented and virtual realities are transforming the field of architecture by allowing architects to convert CAD models into photorealistic renderings and AR scenes. For instance, CAD (computer-aided design) allows people to immerse themselves in life-size plans while drafting, ensuring superior design space exploration.
As well as reducing turnaround times, AR and VR technology streamlines the design process since all project members can access virtual models immediately. Through augmented reality, architects can provide prospective buyers with an accurate view of the future construction by viewing models from various angles. For example, a smartphone, tablet, or mixed-reality glasses can display a full-scale model when the foundation is not in place.
Furthermore, augmented or virtual reality can provide customers with guided tours when they cannot visit the construction site in person. Real estate companies show a design and customize surroundings accordingly. Furthermore, 3D models or immersive experiences can be used to help sell properties, including galleries, tourist attractions, shows, and more.
Challenges with XR
While extended reality development holds tremendous potential for various industries, it also presents a few challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some of the critical issues that hinder complete XR adoption.
Despite the rapid digital advancements, XR performance still relies on other novel hot-point technologies like computer vision, IoT, AI/ML, 3D graphics, and many more. As adjacent technologies continue to improve, the potential of XR to deliver realistic and valuable experiences will also increase, delivering industry-critical outcomes.
The use of XR devices results in accumulating a significant amount of user and environmental data, which can compromise anonymity or even lead to identity theft. Additionally, with XR systems being connected to various platforms, such as social media, for enhanced immersion and convenience, these connected platforms can be compromised or misused, posing a significant privacy risk.
Due to XR’s relative youth, its hardware and supporting systems are more expensive than traditional technologies, often requiring more time to show considerable ROI. However, most of the costs associated with XR are upfront, including hardware and development expenses, making it a favorable long-term investment.
The development of immersive technologies and graphics capabilities makes it more feasible to create highly realistic virtual versions of people without their consent, raising questions about their legality and morality. Thus, the portrayal of violence, pornography, and other similar concepts in immersive virtual environments should be strictly regulated.
With the development of lightweight and compact devices, XR will become more accessible, immersive, and sophisticated, ensuring more natural interfaces, better graphics, and increased comfort. The future of extended reality is exciting as XR becomes more advanced and accessible, offering new applications and use cases that will transform how we interact with novel technologies across various industries and domains.

Rate this article:
4.8/5 (45 reviews)









Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.