Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.



How to make a delivery service app? Actually, that’s not the first question you should be asking. The key question is: “Is there a real demand for your on-demand app in the market?” A lack of understanding of what’s happening on the market will inevitably lead to on-demand delivery app development without clear direction. The result is an app that no one uses, money is wasted, and competitors are rapidly moving forward while your product is stuck in place. How do you make sure your app doesn’t end up as a costly misfire?
First, analyze your competitors. Consider that merely copying existing models, such as Zepto or DoorDash, won’t set your app apart. Ignoring their offerings is worse, however, because it might blind you to their strengths and weaknesses in your competitor’s strategies.
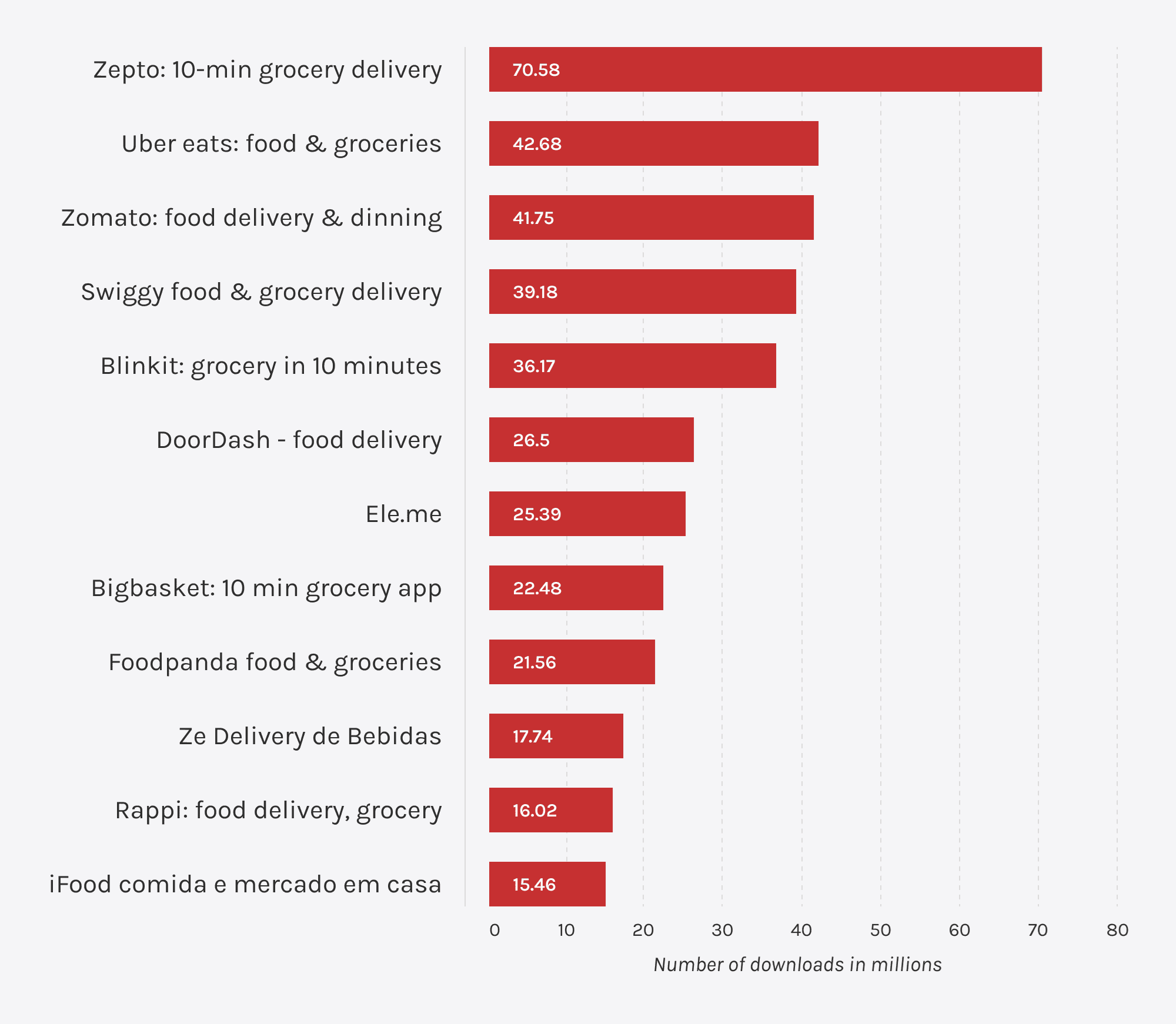
Instead, you should scour the marketplace for opportunities to identify underserved markets or gaps in service quality that can lead to this magic, much desirable UVP, or unique value proposition. A USP is an unmet need or existing offering that needs improvement. Filling this gap will help you stand out and create a space in a saturated market.
Once you’ve defined your UVP and are ready to start food delivery mobile app development, the next big question is how you actually build your app? And this question is just an impulse for multiple others. The first ones are:
As I see it, every option has its pros and cons regarding costs, speed, scalability, and long-term flexibility. The concern here is that these choices will affect not just your short-term on-demand courier app development schedule but the app’s lifetime value and success potential. That’s why this gives some food for thought.
Building an in-house team sounds great — complete control, long-term vision, and deep product knowledge. But let me be honest, it looks solid on paper. Recruiting top talent, covering salaries, benefits, and operational costs, and managing fluctuating demand can be hard to sustain in the long run.
Even so, this approach works best for companies with complex products, evolving roadmaps, and a need for non-stop improvements. If you are trying to achieve consistent growth with additional feature development, then an in-house team is a well-thought choice.
| Pros | Cons |
| Direct control over product development | Lack of specialized expertise |
| Faster communication and problem-solving | High fixed costs |
| Great for continuous development | Time-consuming hiring process |
Outsourcing your delivery app development can save time, minimize costs, and give you access to niche proficiency — especially if you need a logistics-heavy app. Instead of spending months hiring an in-house team, you can work with experienced developers who have already built similar solutions.
A brief checklist for selecting a reliable food delivery app development partner:
Keep in mind that pricing can differ based on region. In this article, I’ve broken down the mobile app development costs, including comparing outsourcing rates across different areas.
| Pros | Cons |
| Faster time to market without hiring delays | Limited control |
| Cost-effective solution with predictable pricing | Quality risks |
| A dedicated team with relevant experience | Vendor lock-in |
“If you’re going in-house, know that you’re signing up for a long hiring process, steady payroll, and the ongoing cost of keeping your team sharp and supported. Start with a lean team that covers the essentials, and bring in external experts for specialized roles like UX design, security, or complex backend development.”
Without a well-thought-out business model, you risk poor margins, operational headaches, and limited growth. Pause and carefully consider the way your app runs, earns money, and scales over time. That’s the winning move.
Online food delivery app development can be a lucrative venture, but profitability depends on the chosen business model, revenue streams, and operational efficiency.
| Model | Advantages | Challenges |
| Single-store app |
|
|
| Aggregator app |
|
|
| Hybrid model |
|
|
Pickup and delivery app development costs vary based on app complexity, features like real-time tracking, and integrations with payment and mapping services. To maximize ROI, businesses should balance upfront costs with long-term scalability.
How to choose? To pick the right model, ask yourself these questions. Here’s a final decision framework:
Knowing your resources, customer expectations, and operational capabilities enables you to choose a model that best uses your time, efforts, and budget.
Diverse business models give rise to app models that cater to the specific needs of different businesses, which goes beyond just getting takeout. The food delivery industry is evolving from aggregating restaurants to B2B supply chains. Let me show the most popular types of delivery applications.
Restaurant aggregator apps connect users with multiple restaurants, making money through a commission for each order placed. This model relies on a vast network of partner restaurants along with enduring marketing and competitively priced services to stay profitable. Best known are Grubhub and Uber Eats.
Dark kitchens, or ghost kitchens, ditch the dining space entirely — they’re built to cook, pack, and deliver food fast, with everything happening behind the scenes. Having overhead costs associated with traditional restaurants cut, this model maximizes efficiency but demands significant investment in kitchen infrastructure and digital marketing to attract customers.
Full-service food delivery apps handle everything from order management to logistics and last-mile delivery. While this approach provides complete control over the business, it also requires substantial investment in fleet management, real-time tracking, and customer service.
B2B food delivery apps focus on wholesale supply, connecting restaurants with suppliers for bulk ingredient purchases. This solution offers high transaction values and recurring revenue streams yet demanding strong supply chain management and logistics coordination.
Grocery delivery apps connect users with supermarkets and convenience stores, allowing them to shop for essentials from home. Platforms like Instacart generate revenue through service fees, markups, or subscription models. Success in this space requires optimized delivery routes and partnerships with major retailers.
Every great idea needs a well-defined revenue plan from the start. The delivery apps’ revenue models span from restaurant commissions to delivery and premium subscriptions. Some even offer advertising spots for businesses looking to boost visibility. This table provides a quick overview of each model’s core aspects, helping you assess their potential impact on your business.
| Model | Overview | Pros | Cons |
| Delivery fee | Customers pay a fee based on distance or service level for each delivery order. |
|
|
| Commission-based | Restaurants or stores pay a percentage per order processed through the platform. |
|
|
| In-app advertising | Restaurants and brands pay for promotional placements within the app. |
|
|
| Marketing fees | Businesses pay for premium listing visibility within the app. |
|
|
| Subscription passes | Users pay a monthly fee for free or discounted deliveries. |
|
|
How to choose? When selecting the right revenue model for your delivery app, consider a framework that evaluates key aspects of your business goals, resources, and market conditions. Here’s how to approach the decision:
Do you know that most food delivery apps fail not because of low-quality coding? Instead, it is a result of a law-quality business strategy. Success here relies on anticipating the challenges that may come up well before the food delivery application development. Build first and troubleshoot later, and you’ll fall into the trap of inflexible, high-risk project approaches — dealing with unsustainable unit economics, rapid churn, compliance nightmares, and scalability roadblocks.
If businesses pour budgets only into acquisition, it’s not enough for long-term business success. Over time, they only put themselves at a risk where they can passively watch users slip away. What’s the solution? Invest in retention. Instead of chasing new customers endlessly, create a digital space where those existing customers feel valued. AI-driven personalization turns one-time orders into habits, while subscriptions and loyalty programs keep your brand top-of-mind without aggressive sales tactics.
Think of retention not exclusively in the context of customers, but consider that for couriers, it matters, too. Couriers can be motivated through gamification and other rewards that help them feel appreciated and valued as part of the business. The happier couriers, the happier customers.
Expanding too soon can do more harm than good. A smarter approach? Master one market before expanding; wait until your tech stack and logistics work synergistically to support growth without disruptions. Design your platform with M&A (mergers and acquisitions) readiness to attract buyers, investors, or partners. M&A implies a tech stack that can grow without constant fixes. It includes clear financial records that make it easy for investors to understand your business. Efficient operations that don’t depend on you being involved in every decision. That also matters.
A rigid MVP might seem like a fast way to launch, but faster doesn’t mean better when user demand spikes and costly rewrites become inevitable. A monolithic architecture can just as quickly become a bottleneck — slowing development, limiting scalability, and making even minor updates risky. And when demand spikes or features grow complex, migrating to microservices isn’t a flip of a switch. It often leads to downtime, tangled operations, and spiraling costs. What to do instead? Put your money into event-driven architecture to handle real-time updates easily, use modular design principles for long-term flexibility, and bring in an experienced architect from day one to scale without costly surprises.
What if you jump right into niche sectors like alcohol and pharma and ignore their particular compliance regulations? Expect penalties, lawsuits, and even having your business operations suspended. What do I recommend? Thoroughly research industry-specific regulations before launch! Work closely with legal experts or outsourcing partners with relevant expertise like Innowise to avoid unpleasant consequences.
A large number of businesses appear to overlook the order density per square mile, which results in higher delivery costs that eat away at their profit margins. Also, over time, things like refunds, driver incentivization, and unsuccessful deliveries add to the hidden costs that affect profitability in the long run.
Is it possible to stay profitable at scale? Absolutely! Measure Customer acquisition cost (CAC) versus Lifetime value (LTV) to make sure you’re building a sustainable business. Focus on high order density to lower delivery costs per order and account for all operational expenses, including driver incentives, chargebacks, and customer refunds.
Bad route planning results in extended delivery periods, annoyed clients, and decreased sales — all of which businesses don’t want to experience. Like always, I recommend using a strategic approach to keep costs, customer satisfaction rate, and revenue in balance.
Implementing AI-powered dispatching allocates drivers based on real-time conditions, not just distance. Using predictive analytics to adjust pricing dynamically and enable real-time rerouting and delay predictions to prevent bottlenecks and increase reliability.
“The on-demand delivery business has its ups and downs. When things run smoothly, you may see fast deliveries, loyal customers, and happy couriers. Yet, other factors such as spikes in demand, technology hiccups, and high driver turnover are equally part of the mix. That’s where AI and data are your helping hand. Smarter routes, demand predictions, and personalized experiences keep things efficient and competitive.”

Head of Big Data and AI
With an MVP, there are pitfalls to watch out for. Let’s say you embrace the notion that more is better, and overwhelm your on-demand delivery app with every possible feature for the first version. What’s around the corner? Soaring costs, slipping deadlines, and a clunky product no one enjoys using.
Otherwise, you may swing too far in the opposite direction, cutting critical features to launch faster and cheaper — only to face low adoption rates and frustrated users who abandon the product.
Finally, you can be one of those who don’t plan for growth, building features that work at a small scale but crumble when the user base expands.
Think of what minimum is needed to test product-market fit. Prioritize those features and leave the extras for later iterations. Remember that every component should work hassle-free for everyone involved: users, couriers, or business operations. This approach keeps development lean, reduces risks, and delivers a functional yet scalable product. At Innowise, we help businesses avoid these hurdles by building MVPs that focus on essential features.
Customers claim a fast, simple, and reliable process from start to finish. No matter what they do — browsing options, placing an order, or tracking their delivery — convenience is key. Clear communication and flexibility throughout the experience make users satisfied at every stage. Here are the key features that delivery apps could include:
For couriers, a successful app means they can deliver more orders in less time and with fewer complications. Easy navigation, real-time updates, and simple order management tools contribute to this much-needed excellent user experience. The following features are a must for making courier’s work productive:
Admins manage the full operation, optimize performance, and act as a key connector between customers, couriers, and businesses. Admins can maintain control, track performance, and improve service quality if the following features are available:
Innowise has successfully delivered on-demand app development projects, including a custom-built food delivery app packed with features outlined above. A popular restaurant chain in Europe faced the following challenge: while foot traffic remained solid, they struggled to grow revenue and retain customers. With more people opting for food delivery over dining out or cooking at home, the client realized they needed more than just a presence on third-party delivery platforms.
They approached us, and we have developed a complete food delivery ecosystem that includes iOS and Android apps, a full-featured website, and a loyalty program implementation.
Key features included:
As a result, the client saw a 25% increase in revenue, over 500 loyalty cards issued, and ongoing improvements based on user feedback. The solution continues to evolve with support from the Innowise team.
The technology stack determines how well your app performs under pressure, handles a growing user base, and integrates with other systems. A poorly chosen tech stack can hinder scalability, increase costs, and create inefficiencies that complicate future updates and integrations.
For example, choosing a tech stack based solely on familiarity rather than scalability can limit your ability to scale efficiently in the future. Opting for a monolithic backend architecture can lead to slower development cycles and scalability issues as the app grows and adds more features.
For the frontend, aim for frameworks that enable cross-platform development or consider native solutions if targeting specific platforms. The right choice will depend on your goals for user experience and performance. Frontend: React Native, Flutter, Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android), .NET MAUI.
When choosing backend technologies, ensure that they can handle real-time requests and scale as your app grows. Opt for technologies that are known for their efficiency and performance in handling large amounts of data or high user activity. Backend: Node.js, Python, Go, C#.
As for databases, pick a system that can manage your data’s needs, whether it’s relational, NoSQL, or requires real-time syncing. Database: PostgreSQL (relational), MongoDB (NoSQL), Firebase (real-time sync).
Select a provider that offers scalable, reliable, and secure services to support your app as it grows. Cloud infrastructure can help make operation smooth as user demand increases. Cloud hosting: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure.
Consider using services that provide accurate and real-time data for on-demand delivery tracking and maps. These services will be essential for features such as delivery tracking or geo-based functionalities. Maps & location tracking: Google Maps API, Mapbox.
For payment processing, choose reliable, secure, and widely accepted platforms to facilitate seamless transactions within the app. Payment processing: Stripe, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay.
Think of push notifications integration? Decide on tools that ensure timely, personalized, and non-intrusive messages. Push notifications: Firebase Cloud Messaging, OneSignal.
Finally, for AI-driven analytics, implement tools that help gather insights, optimize user experience, and make data-driven decisions to improve the app’s performance. AI-driven analytics: TensorFlow, ML Kit, AWS SageMaker.
To make sure that your app’s scaling capabilities are optimally designed, avoid a single third-party provider or specific cloud service to limit vendor lock-in, which will improve scaling flexibility down the road. Utilizing containerization with tools like Docker and Kubernetes helps create scalable, consistent deployments across different environments. Using an API-first strategy improves integration capabilities with outside services or platforms, so your app is able to change, grow, and add new functionalities without extensive changes to the architecture.
How to create a food delivery app that will be profitable, scalable, and popular? The restaurant delivery app development takes careful planning, the right tech stack, and a solid focus on scalability. Sounds simple when it’s all laid out in a guide like this, right? But in reality, you’ll hit some roadblocks along the way. That’s where we come in — not as partners in crime, but as your go-to team for building a rock-solid platform that gets the job done. If you’re ready to bring your idea to life, let’s discuss how to make on-demand delivery app just for you.

Head of Mobile
Eugene drives our mobile vision with a sharp eye on performance, usability, and future-proof tech. He helps businesses turn big ideas into fast, intuitive apps that people actually want to use.












Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.