Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.


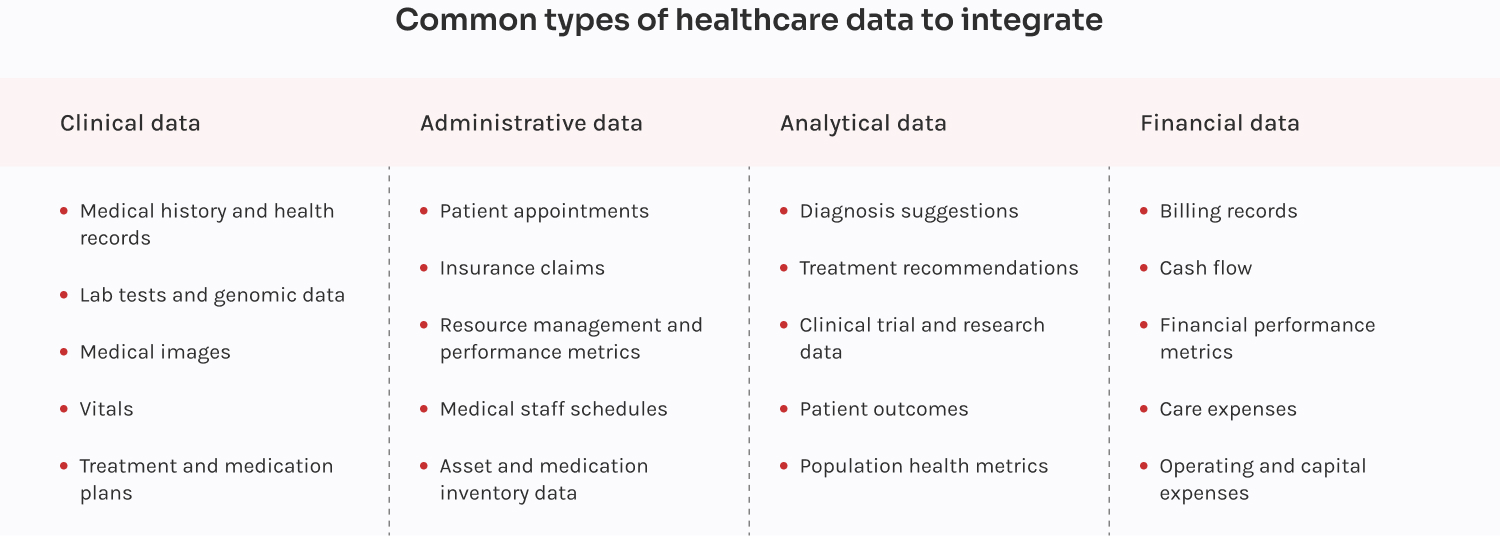
Healthcare data integration brings together information from disparate IT systems, giving medical organizations holistic data management capabilities and a 360-degree view of their data.
Now, integrating healthcare information is more crucial than ever. Annually, providers generate around 30 petabytes of data — clinical, administrative, analytical, and financial. However, almost half of it (47%) remains underutilized when delivering care and business decisions. Thanks to integration, healthcare businesses can tap into all that valuable information scattered across various systems without letting any significant details fall through the cracks.
Aside from the mismatch between data volumes and data utilization, other factors contribute to the rising need for healthcare data integration.
According to PwC, about 81% of healthcare providers have adopted cloud solutions, so medical professionals are getting used to more convenient data access. API-centric medical apps also set the bar high, offering a glimpse into truly integrated healthcare data. These factors contribute to the growing need for organization-wide data integration.

The adoption of telehealth has increased in recent years, and now the technology is used for various medical specialties — primary or urgent care, mental health, cardiology, endocrinology, etc. In the years to follow, care digitization will only grow, venturing into remote surgery and diagnostics realms. It will spur demand for comprehensive patient data that can be conveniently accessed during online consultations.

The healthcare AI market is predicted to expand at a 37% CAGR between 2024 and 2034, reflecting the growing confidence in predictive, prescriptive, and generative artificial intelligence among the medical community. To distill reliable insights with AI, healthcare data integration is a must, and many medical organizations agree — 55% plan to aggregate unstructured data for further analytics.

Recently, there’s been a much bigger focus on tailored care, accelerated by advances in precision medicine and push for better health outcomes. To personalize care, medical institutions must integrate multiple data points — everything from patient-generated health information to medical history collected by different providers — and it incites the need for data integration.

Government agencies continue to develop regulatory frameworks supporting interoperability standards, like HL7 or FHIR, necessary for healthcare data integration. This has led to steady growth in their use. According to the National Survey of Health Information Exchange Organizations, now more than 80% of healthcare organizations share HL7 v2 messages, and 22% use FHIR APIs for data exchange.

Recent government initiatives and incentives boost the adoption of HIE (health information exchange) software across the healthcare industry, driving the market CAGR of 9.7% from 2024 to 2030. This regulatory push also stimulates new medical data integration projects among the providers, making data sharing with partnering organizations more seamless than ever.

Using wearable medical devices proved to be an efficient way for doctors to continuously monitor patient state, compared to in-person assessments and manual vitals tracking. By integrating the device-collected data in patient care, healthcare providers can tackle the onset of chronic diseases, avoid disease complications, and improve treatment outcomes.

The regulatory oversight in the healthcare domain becomes even more rigorous, especially regarding data privacy. Storing data in disparate systems with different security measures in place puts data privacy at risk, so it further encourages data integration in healthcare.

The global healthcare blockchain market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 63.3% from 2024 to 2030, with a substantial market share belonging to health records storage and exchange solutions. When used to manage integrated medical data, blockchain enables exceptional data access transparency and reliability.

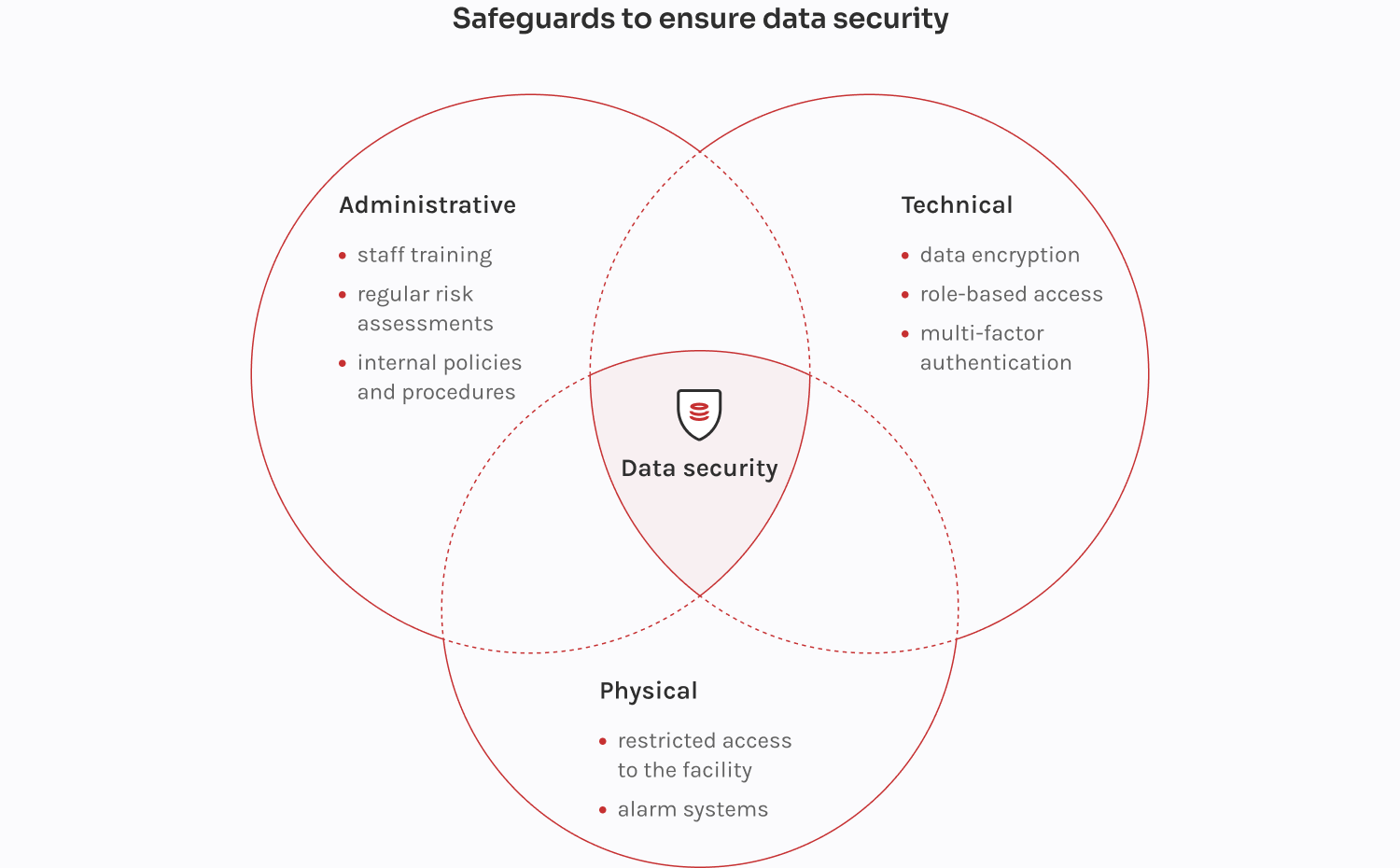
Core security measures for healthcare data integration include SSL and TLS-based data encryption (both in transit and at rest) and API authentication mechanisms, like OAuth or API keys. To add a new layer of security for health data, it’s a good practice to employ data masking during integration testing or data transfer, as well as data segmentation based on sensitivity level.
When integrating healthcare data across systems, HIPAA-compliant hosting providers like Atlantic.Net ensure secure and scalable infrastructure for seamless interoperability.
Security measures do not stop after the healthcare data integration. Automated security monitoring systems — like SIEM and RMM — will help keep an eye out for security threats, detecting vulnerabilities and unauthorized data access attempts in real time. Regular patch management, penetration testing, security and compliance audits will help proactively identify and tackle any compliance risks that may eventually lead to hefty fines.
Real-time access to cohesive patient data empowers better diagnostic and treatment choices, leading to better health outcomes. 25% of clinicians agree that integrated data platforms enable better decision-making.
Healthcare data integration helps streamline administrative processes: less time is spent on data entry, routine paperwork, compliance and performance reporting, and physicians’ focus is redirected to patient care.

Integrating data collected by various IT solutions ultimately leads to lower operational expenses. 30% of healthcare providers report that aggregated data platforms lead to cost savings thanks to better resource allocation and workforce management.

Thanks to HIE adoption, different healthcare providers can access complete patient records, make informed diagnostic and treatment decisions based on reliable data, and avoid unnecessary medical procedures.

Since the data exchange between applications is performed automatically, the risks of data errors and data duplication are minimal compared to manual data entry and sharing.

Integrated databases with anonymized patient records can fuel clinical studies, including those related to disease patterns, medication side effects, treatment protocol improvements, and population health management.

84% of patients agree that having their records available online improved their communication with healthcare providers. Instant access to consolidated health records promotes health awareness and helps patients become more engaged in treatment.

Challenge
Solution
Harness the power of data mapping during integration
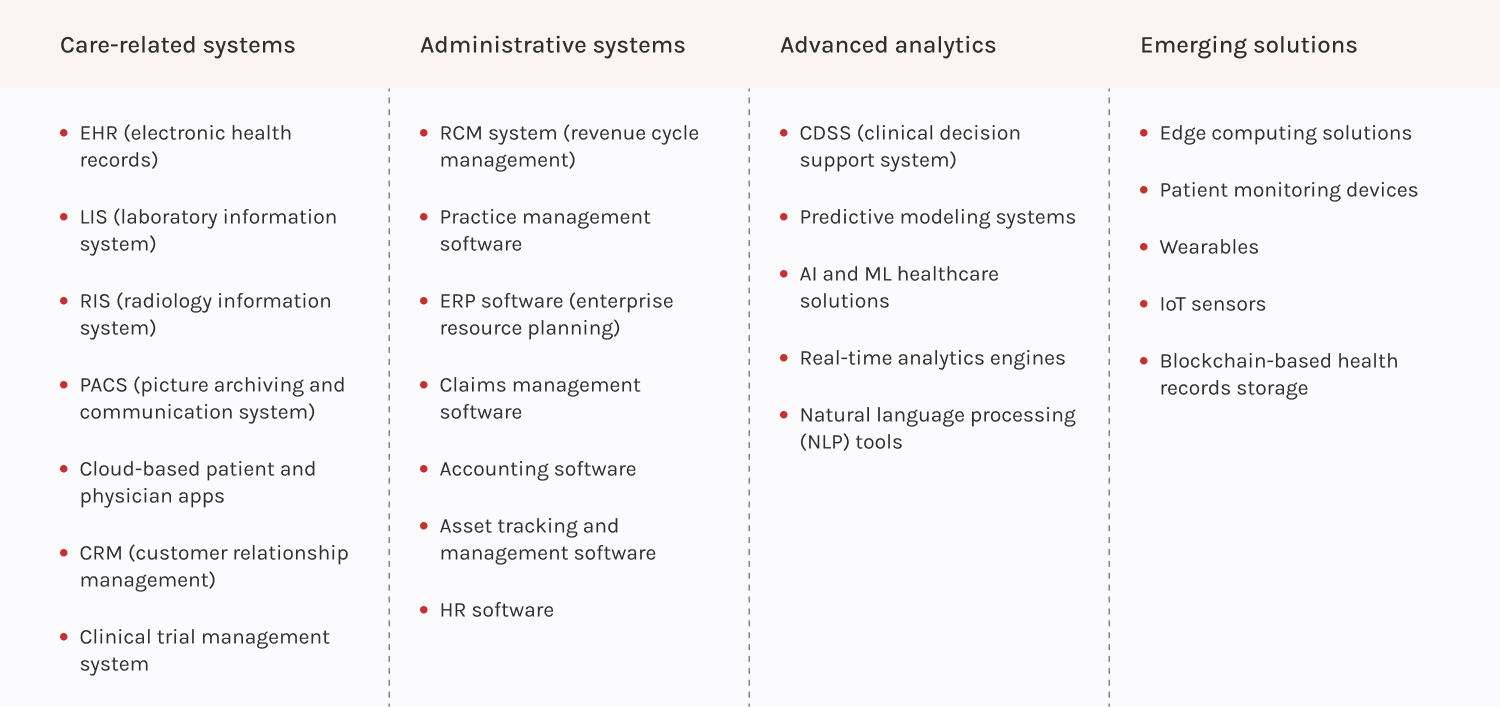
Now, healthcare data integration is going mainstream, particularly when it comes to connecting applications with EHR systems, aggregating data for advanced analytics, or consolidating patient vitals from medical devices. The benefits of healthcare data integration are clear — by aggregating healthcare data into one centralized platform with standardized data, providers get a full picture of the medical records. They also can offer personalized and patient-centric services, better coordinate care, and improve decision-making and organizational efficiency.
Even though the healthcare data integration process does come with challenges — particularly around security, compliance, and interoperability — it shouldn’t prevent medical organizations from integrating their data. Engaging an experienced vendor offering healthcare data integration services can help navigate these challenges and ensure the integration is done securely and efficiently.











Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.