Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.



Blockchain adoption is accelerating across industries, transforming how organizations record, share, and verify data. Initially known as the foundation of FinTech, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs, blockchain now plays a growing role in healthcare, e-commerce, public services, and logistics.
In 2020, the worldwide blockchain supply chain market was valued at $253 million. By 2026, it is projected to grow to $3,272 billion, showing an incredible CAGR of 53.2%.
Blockchain technology in the supply chain provides a more secure and comprehensive way to track transactions. Through a temper-resistant distributed ledger, companies can oversee a product’s history from its origin to its current location while securely documenting each iteration from manufacturing to sale. And these capabilities show how blockchain technology impacts supply chain performance.
With this shared digital infrastructure, supply chain partners can reduce manual errors, time delays, and costs linked to intermediaries. The technology also strengthens traceability and makes it easier to identify potential fraud or data inconsistencies. As a result, blockchain technology impacts supply chain performance by enabling trusted collaboration, synchronized logistics, and faster settlements without overhauling existing systems.
In this article, I’ll explain why blockchain holds great promise for managing stable, predictable supply chains and how it can help companies overcome business challenges. We’ll also break down the most practical blockchain use cases supply chain leaders can implement right now.
Blockchain for supply chain means transactions are initiated by authorized participants or smart contracts triggered by a pre-defined event. For supply chain security, permissioned blockchains are generally used, allowing only members with special rights to validate data.
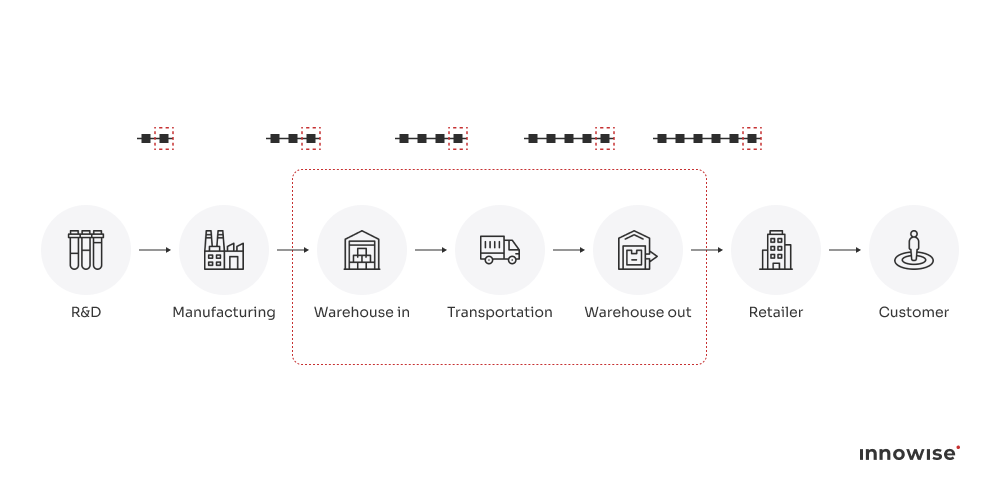
Blockchain data is stored chronologically in timestamped blocks after validation and encryption through a hash function. As a result, a distributed ledger provides a reliable source of truth to oversee supply chain activities and authenticate inventory origins. Below, we explore the most impactful blockchain supply chain use cases driving transparency, trust, and efficiency across industries.
Blockchain technology in the supply chain gives every participant access to a shared, tamper-evident history of item movements and transactions. This lets teams verify origin, transformations, and custody without reconciling siloed records. Many organizations pair it with GS1 standards such as EPCIS to standardize event data and achieve true end-to-end visibility.
Around 54% of international logistics providers report using blockchain-based tools to improve supply chain transparency and security. These implementations have contributed to a 36% drop in documentation errors and a 31% reduction in counterfeit activities across global networks.
A well-known example is Walmart, which uses blockchain in supply chain management to trace the origin of its mangoes. What once took nearly a week now takes just 2.2 seconds, allowing for fast, targeted recalls during foodborne illness investigations.
Retail giants, the Aura Blockchain Consortium, which includes luxury brands such as Louis Vuitton, Prada, and Cartier, uses the same principle to verify product authenticity. Each item receives a unique digital identity that customers can scan to see its full history from production to sale, helping fight the multi-billion-dollar counterfeit market. Similarly, De Beers tracks diamonds on a blockchain from mine to retailer, ensuring each stone is ethically sourced and conflict-free.
Blockchain for supply chain management maintains a single, tamper-proof record of every stock movement across suppliers, warehouses, and retail outlets. Instead of relying on isolated spreadsheets or mismatched ERP entries, all participants see the same verified data, from raw materials entering production to finished goods reaching distribution hubs. On top of this shared ledger, an AI layer monitors activity in real time. It spots issues like sudden stock drops, items in the wrong location, or irregular lead times. When something looks off, the system flags it and suggests actions such as adjusting safety stock or reorder points.
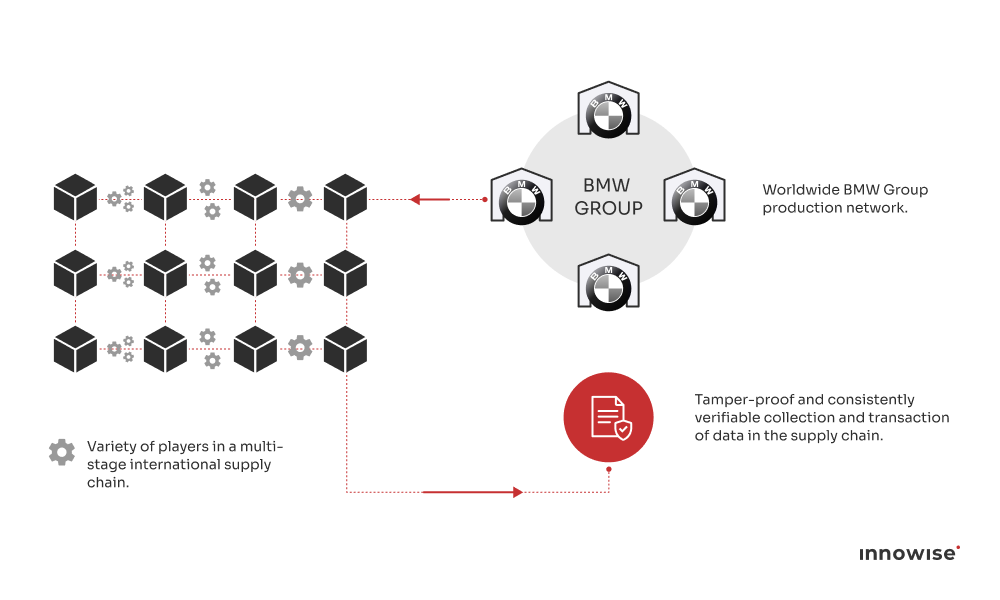
For example, automotive manufacturers such as BMW use blockchain platforms to track parts inventory across plants and suppliers. Every component is logged on the ledger when received, assembled, or shipped, which helps production planners detect shortages early and avoid costly line stoppages. In retail, Home Depot applies a similar approach to manage supplier deliveries. Blockchain timestamps each inbound shipment, reducing disputes over missing or delayed items and improving shelf replenishment accuracy.
Security issues in traditional supply chains are widespread. According to IBM’s 2024 Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach in the manufacturing sector reached $4,73 million, with third-party risks identified as a growing factor. With blockchain technology in supply chain management, companies can verify vendor identities, certifications, and material sources before onboarding or approving shipments, significantly lowering exposure to compliance and reputational risks.
For instance, automotive leader Renault Group uses a blockchain platform to manage more than 20 suppliers’ compliance documentation. This approach ensures each component meets industry and environmental standards before entering the production line.
In practical terms, blockchain helps companies monitor supply networks for anomalies, such as sudden changes in supplier activity or mismatched certification data, and triggers alerts for investigation. Combined with AI analytics and IoT sensors, it enables a proactive approach to risk detection, transforming fragmented compliance management into continuous, verifiable oversight.
Coordinating goods, pricing, documentation, and payments across multiple parties often stretches settlements over several days or even weeks. Blockchain streamlines this process by placing trade data and milestones on a shared, tamper-evident ledger and by using smart contracts to trigger payments automatically once predefined conditions are met.
In letters of credit, banks have seen major cycle-time reductions after shifting workflows to blockchain networks. ING’s pilots and later adoption on the Contour platform, for example, cut LC processing times from 5–10 days to under 24 hours in some cases, driven by digitized document exchange and synchronized approvals.
In open-account and commodity trade finance, blockchain is reshaping how documents and data move between parties. Platforms like Komgo show what that looks like in practice: traders and banks can share digital trade documents and KYC data securely, cutting down duplication and reducing the time it takes to approve financing.
The same logic is now extending beyond trade finance. Institutional and manufacturing clients are starting to issue their own stablecoins or settlement tokens to manage payments with suppliers and partners. In these systems, transactions take place directly on the chain, with blockchain acting as the built-in settlement layer that connects documentation, payments, and reconciliation.
Our expertise in building blockchain-based financial systems extends beyond enterprise settlements. For instance, we developed a mobile cryptocurrency portfolio management app for a European DeFi company that allows users to track, trade, and exchange crypto assets in real time. The app includes in-app wallets, live market data, and two-factor authentication, providing a secure and intuitive way to manage digital assets while reflecting the same transparency and efficiency blockchain brings to global trade.
Supply chains run on documents: purchase orders, certificates, invoices, and bills of lading. Blockchain helps keep every version clean and trustworthy by giving each file a unique fingerprint, a timestamp, and a clear record of who touched it and when. Teams see the same source of truth, so duplicates and quiet edits stop slipping through.
Picture a shipment where the invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin move between a supplier, a forwarder, a bank, and customs. Each document is registered with its fingerprint. If someone changes a value or uploads the wrong file, the mismatch shows up immediately. Approvals move faster, exceptions get flagged, and audits stop being a scramble. You can tighten privacy without exposing sensitive data. With zero-knowledge proofs, a party can confirm a claim without revealing the underlying document.
Our team applied these principles in our projects. For example, for a major German telecom provider, we created a blockchain-secured document system with an RAG chatbot that boosted employee productivity by 41% and improved breach detection by 20%. Also, in partnership with CoreLedger AG, we built a cross-platform app for creating, signing, and verifying documents with cryptographic protection and timestamping.
Logistics involves manufacturers, carriers, customs, and warehouses, with each handoff creating new data and documentation. Blockchain keeps that data consistent and transparent by recording every shipment event in one tamper-proof ledger. All parties access the same verified information, reducing delays, eliminating mismatches, and keeping cargo on schedule.
At the Port of Rotterdam, for example, blockchain pilots log container movements and cargo documentation in real time. Each gate-in, customs clearance, and loading step is instantly recorded, cutting handling times and reducing manual checks. DHL and Accenture tested a similar setup for international shipments, timestamping each transfer to resolve disputes over damage or delays before goods reach customers.
When paired with IoT sensors, blockchain adds full visibility into storage and transport conditions. Data on temperature, humidity, and routes is captured automatically and appended to the record. If readings go beyond safe limits, operators receive immediate alerts, helping protect sensitive cargo such as pharmaceuticals and perishables.
“The supply chain gains a single, verifiable record of origin, custody and payments with blockchain. At Innowise, we deploy production systems that integrate with your ERP and logistics, lower reconciliation costs, speed recalls and settlements, and prove ROI with clear KPIs.”

CTO
We’ve seen what blockchain can do; now let’s see how it plays out in real-world industries. Logistics, retail, agriculture, energy, and oil and gas use blockchain for end-to-end traceability, authenticated documents, automated settlements, and verified partners. If you are planning an implementation, our whitelabel blockchain core solutions and custom builds help you launch secure, tailored platforms quickly.
Blockchain provides a shared, tamper-proof record of every shipment event and document across the logistics chain. With a single source of truth connecting ports, carriers, customs, and warehouses, teams can reduce errors, expedite handoffs, and remain fully audit-ready.
Shipment milestones, like gate in, gate out, vessel load, customs release, warehouse receipt, and final delivery, are logged on a permissioned ledger. All parties access a shared timeline in real-time, which leads to better ETA information and coordination.
Systems hash and timestamp bills of lading, commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates. Stakeholders can verify document integrity without emailing versions or reconciling edits. And customs authorities can validate provenance and chain of custody with greater speed and confidence.
Smart contracts automatically flag missed cut-offs, temperature breaches, or SLA overruns. The contract logic manages payments, holds, or credits based on verified shipment events, reducing delays and ensuring accountability across the supply chain.
Companies store KYC and compliance data for carriers, NVOCCs, brokers, and 3PLs on shared ledgers. Verified identities and reusable credentials simplify partner onboarding, boost approvals, and decrease fraud risk.
Sensors continuously send temperature, humidity, shock, and location data to the ledger. Authorized parties see exceptions in real time, helping safeguard pharmaceuticals, perishables, and electronics from damage or spoilage.
An immutable event trail and document proofs shorten claims cycles for shortages, damages, and delays. Auditors can review the same authoritative history without stitching together records from disconnected systems.
AI agents use verified shipment data and IoT signals from the ledger to spot anomalies, predict delays, and launch the right actions automatically. They can trigger alerts, reroute shipments, schedule inspections, or start claims without waiting for manual input. This setup turns the shared ledger into a live control layer that speeds up decisions, reduces manual checks, and keeps every step connected to trusted, traceable data.
Blockchain gives retailers, suppliers, and customers a shared, tamper-evident record of product data. The system tracks provenance, handling steps, and certifications across stores, distribution centers, and partner networks. Teams run audits faster, manage recalls with precision, and maintain trust throughout the supply chain.
Each SKU carries a digital identity tied to its blockchain record. Shoppers and store teams can scan products to see verified details such as origin, batch information, processing stages, and chain of custody.
Production lots, inspection results, and shipment events are logged on the blockchain. When issues arise, teams can identify and remove affected batches quickly, which reduces risk and minimizes disruption.
High-risk products such as luxury goods, electronics, and pharmaceuticals receive a unique digital ID linked to a blockchain record. Store staff and customers can scan a QR or NFC tag to verify authenticity and view origin, batch details, and custody history.
Each supplier records delivery accuracy, product quality, and certifications on a shared blockchain. Category managers see up-to-date performance data and verify compliance instantly, without sorting through separate systems or documents.
Smart contracts release payments, rebates, and chargebacks only when verifiable conditions are met, such as being delivered on time, shelf-life within limits, or promotion terms satisfied. Finance teams gain faster closes, fewer disputes, and clear audit trails.
Each returned item is checked against its on-chain identity and event history. Retailers confirm authenticity instantly, reduce fraudulent returns, and make faster decisions on refurbishment or restocking.
Walmart, an American multidimensional retail corporation, has enhanced supply chain transparency and provenance tracking by utilizing blockchain technology. Employing a decentralized database, Walmart can identify the source of foodborne illnesses and contamination, ensuring optimal food monitoring, traceability, and safety. With blockchain technology, Walmart can ensure product quality, reduce costs, and promote accountability, quickly identifying and discarding affected foods before they reach the consumer.
Furthermore, Walmart allows customers to scan products in-store and obtain immediate information on their origin and logistics processes from source to retail outlet.
Transportation networks connect carriers, brokers, shippers, and regulators through many moving parts. Blockchain creates a shared, tamper-evident record of routes, handoffs, and documents. Everyone works from the same verified data, improving tracking accuracy, cutting paperwork, and keeping coordination fast and transparent.
A permissioned ledger captures GPS data, route updates, stops, and dwell times in real time. Dispatchers and customers see verified route data in one place, so they can track shipments accurately without comparing multiple systems.
Blockchain secures transit permits, customs declarations, and insurance certificates with hashes and timestamps. Each party can instantly confirm that documents are authentic, reducing delays and manual checks during border clearance.
With blockchain, every inspection, repair, and part replacement is recorded in a single verified ledger. Buyers, auditors, and service centers can review the full maintenance history to confirm authenticity and ensure regulatory compliance.
Telematics data connects directly to blockchain smart contracts, adjusting premiums and processing claims automatically. Verified events such as hard braking or collisions trigger transparent, traceable workflows for faster settlements.
In shared fleets or equipment networks, blockchain records every reservation, access, and usage event in a single, verified ledger. All parties see the same data, which makes billing accurate, reduces disputes, and keeps scheduling simple.
Blockchain links incident reports, sensor data, and corrective actions to one verified record. Investigators and regulators access the same reliable information, which speeds up reviews and strengthens accountability.
The Port of Antwerp-Bruges replaced PIN-code pick-ups with the Certified Pick up (CPu) platform. CPu issues digital release rights and shows the customs status of each container, making cargo handling more secure and transparent. Carriers such as Hapag-Lloyd use T-Mining’s Secure Container Release to transfer these digital rights between parties, removing the need for PIN codes entirely. After its first year, CPu had processed more than one million containers.
Manufacturing consists of many moving parts: suppliers, production lines, logistics partners, and service teams. Blockchain connects all of them through a shared, tamper-proof record of materials, production steps, and quality checks. Every participant works with the same verified data, making it easier to trace components, confirm compliance, and resolve issues quickly. This transparency strengthens quality control, speeds up audits, and improves coordination across the entire supply chain.
Manufacturers use blockchain to trace raw materials and components across every supplier tier. Each transaction records source details, certifications, and compliance data, helping procurement teams confirm authenticity and ethical standards before production begins.
Each high-value component receives a unique digital identity recorded on the blockchain. Assemblers, distributors, and customers can verify authenticity at any stage, which reduces the risk of counterfeit parts entering production or the market.
Every step on the shop floor, from test results to serial numbers, gets logged in one tamper-proof record. If something goes wrong, it’s easy to spot which batch was affected and fix the issue fast, without pulling everything back.
Machine checks, repairs, and part replacements are logged in one verified record. This clear history helps teams spot patterns, plan maintenance before breakdowns happen, and keep production running smoothly.
A time-stamped ledger records bills of materials, firmware versions, and ECO approvals, creating a full audit trail of design changes. That trail establishes IP ownership and pinpoints the configuration and build date for every product run.
Warranty status and service actions reference verified production data. Service centers check each part’s history before approving a repair or replacement, which reduces errors and speeds turnaround.
Blockchain keeps a permanent record of safety checks, environmental data, and sourcing documents. Companies can easily share verified proof of compliance with regulators and customers, reducing audit time and strengthening transparency.
Agriculture involves many stakeholders, including seed partners, producers, processors, distributors, and retailers. Blockchain provides one trusted record for all the parties in each lot, everything from inputs (chemical and biological), field conditions at harvest, the processing steps, and shipment. Teams can trace a product back to the field in minutes, validate certifications, and only recall affected batches. It also streamlines audits and reduces the risk of expensive errors
Blockchain keeps a verified record of every stage, from seed lots and harvest dates to processing and delivery. Buyers and auditors can check where each product came from, how it was handled, and who managed it at every step.
Each product gets a digital record showing its seed source, soil treatments, pesticide use, and feed inputs. Importers can review these details instantly before purchase or border clearance to secure quality and compliance without extra paperwork.
Sensors track temperature, humidity, location, and handling throughout the journey from the field to storage. If conditions go off limits, alerts are triggered, the system sends alerts and logs the event, creating a trusted record of how perishable goods were handled.
Using blockchain, companies can verify sustainability labels like organic, fair trade, or non-GMO. Each certification is stored as proof on the ledger, so retailers and customers can trust the claim without seeing private farm data.
Blockchain can automate how farmers get paid and insured. Once a crop is delivered and quality is confirmed, payments go out automatically. If weather data or sensors show damage, insurance claims trigger right away.
With blockchain, every product batch is traceable from farm to shelf. When a problem appears, teams can immediately see which lots are affected, contact the right partners, and remove only those items to keep everyone informed and minimize waste.
By 2026, the blockchain-in-energy market is projected to exceed $1,56 billion, up from $127,5 million in 2018. Energy companies see clear potential, from smarter grid management to transparent green-energy trading. Blockchain records generation, trades, and settlements in one shared, tamper-evident ledger, so everyone works from the same facts. That clarity improves traceability, speeds up settlements, and makes models like community energy trading and flexibility services practical.
Blockchain lets households and local producers trade energy directly. Every kilowatt-hour is recorded and verified, and smart contracts handle payments automatically. Neighbors can buy or sell excess power within a community grid without middlemen or manual tracking.
Using blockchain, it is easier to prove where renewable energy comes from. Each certificate links to verified generation data, showing when and where the power was produced. Buyers can confirm the source of their green energy without accessing private plant information.
A shared ledger tracks bids, dispatch orders, and what each asset actually delivers. After systems verify delivery, smart contracts pay out automatically. Everyone sees the same record, so manual checks drop and settlements close faster.
A shared blockchain record lists all connected energy assets like rooftop panels, batteries, and smart inverters. Grid operators and aggregators can quickly see who owns each asset and what it can deliver before connecting it to the system.
Blockchain keeps every charging session transparent by recording time, energy use, tariff, and participant IDs on a shared ledger. With everyone accessing the same verified data, charging networks and utilities can settle roaming payments quickly and avoid billing disputes.
Blockchain keeps carbon data transparent by logging emissions, offsets, and certificate retirements in one verified record. Auditors and partners can easily trace where numbers come from, confirm their accuracy, and trust that the data hasn’t been changed.
The industry runs on a long chain of handoffs and paperwork: trades, cargo documents, meter readings, inspections, and payments. Blockchain cuts through the complexity by keeping a single, tamper-evident record of those events. Every party, such as producers, traders, terminals, and banks, works from the same facts, so workflows move faster, disputes drop, and accountability is clear.
Blockchain keeps a clear record of every meter reading, tank check, and lab result. Data like volume, purity, and quality are verified in real time, so ownership and payments only move forward when everything meets the agreed standards.
All shipping documents, like the bill of lading, certificate of origin, and quality reports, sit in one secure record that updates in real time. Voyage events such as notice of readiness, laytime, and cargo completion are tracked automatically. This shared record lets ports release cargo digitally, cutting out PIN codes and long email chains.
Operators log batch IDs, nominations, allocations, and tank-to-tank transfers on a shared ledger. The same record tracks linefill, interface cuts, and blending recipes. All parties see one real-time custody trail without stitching together spreadsheets.
A shared ledger keeps confirmations, contract changes, pricing formulas, delivered vs quoted specs, inspection results, and invoices in one synchronized record. Teams reconcile against the same data, which shortens settlement, cuts delivery disputes, and closes the books faster.
Smart contracts automatically calculate joint-venture splits based on measured volumes and agreed terms. Each partner sees a clear audit trail from field data to final payment, removing confusion and speeding up reconciliation.
Every trade or shipment in oil and gas must pass through strict compliance checks. With blockchain, verified identities, sanctions screenings, and inspector accreditations can be logged on a shared, tamper-evident record. It makes proof of compliance quick and verifiable. No sensitive files moving around by email.
Record flare volumes, methane intensity, LDAR findings, and offset retirements as signed entries linked to specific batches or cargoes. Buyers and financiers can verify ESG data against the same record used for custody and quality.
As a top-tier blockchain development and consulting services provider, Innowise taps into these technology capabilities to embrace supply chain transparency, security, and efficiency. Our vetted developers build smart solutions that bring high ROI, improve operational excellence, and drive revenues. We are dedicated blockchain enthusiasts committed to making the world more technologically advanced through digitization and innovation. Choose us if you are searching for an all-in-one solution that ensures the stability and predictability of your supply chains.

Blockchain expert & DeFi analyst
Andrew is an expert in blockchain and financial technology. His strong background in mathematical modeling and securities market analytics drives his strategic approach. He helps startups and established companies navigate the crypto space, combining sharp tech insight with hands-on business sense.










Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.