Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.


According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), an estimated 2–5% of the global GDP — about $800 billion to $2 trillion — is laundered every year. That’s a mind-blowing amount of dirty money distorting economies, slowing down development, and breaking trust in the financial system. Now, think about this in real-life terms — imagine how many attempts to launder money happen every single day. Pretty terrifying, right?
That’s where AML transaction monitoring comes in. It’s like having a financial watchdog on duty 24/7, keeping an eye on millions of daily transactions — transfers, deposits, and withdrawals — to sniff out anything suspicious. Think of it as the front line in the battle against financial crime, working in real-time (or pretty close) to catch anything that doesn’t add up.
AML transaction monitoring is a fascinating mix of tech, strategy, and vigilance that’s worth knowing about. Ready to dig into the nuts and bolts of it all? Let’s dive in!
$17.59bn
the estimated value of the AML transaction monitoring global market in 2024
source: Fact.mr
9.4%
projected CAGR of the AML transaction monitoring global market by 2024
source: Fact.mr
When it comes to fighting financial crime, AML transaction monitoring is here, analyzing every transaction — big or small — to catch anything suspicious. Why is this so important? Because criminals aren’t obvious about their moves. They use all sorts of tricks like smurfing to break large amounts into small, harmless-looking transactions to fly under the radar. AML systems harness ML to identify unusual transaction patterns, AI-driven behavior analysis to pinpoint activities that deviate from a customer’s normal profile, and sophisticated rule-based engines to flag transactions that breach regulatory thresholds.
In addition to traditional financial systems, cryptocurrencies have added a new layer of complexity to AML efforts. Their anonymity and decentralized nature make them a convenient tool for criminals to launder money or fund illegal activities without detection. Traditional AML methods, like customer checks and suspicious activity reporting, struggle to keep up in this space. That’s why effective transaction monitoring with advanced tools like blockchain analysis and monitoring is so important — it helps identify and stop illicit activity, adapting to the shifting dynamics of the digital financial world.
A strong AML transaction monitoring system analyzes transaction patterns, locations, business types, and more to create detailed risk profiles. These profiles help identify potential exposure to financial crime and adjust monitoring based on each customer’s overall risk level.

The system must offer adaptable rule and scenario configurations. It must not only handle standard patterns and requirements but also let you tweak things to stay on top of changing regulations, industry trends, and new fraudulent tactics.

With updates to compliance rules, reporting requirements, and risk factors popping up all the time, a solid AML transaction monitoring system needs built-in tools to keep up with these shifts automatically.

The system should handle both real-time and ongoing monitoring. Real-time keeps you in the loop with instant alerts for suspicious activity, while ongoing monitoring looks at the bigger picture, spotting trends and patterns over time.

A solid AML transaction monitoring system has automation and advanced analytics working together. Automation takes care of the monitoring process and generating Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs), while advanced analytics dives into the data to spot patterns, trends, and red flags.

The monitoring system should use advanced AI to sharpen detection and reduce false positives. AI algorithms make monitoring faster and more reliable as they can spot tricky patterns and anomalies that traditional methods might overlook.
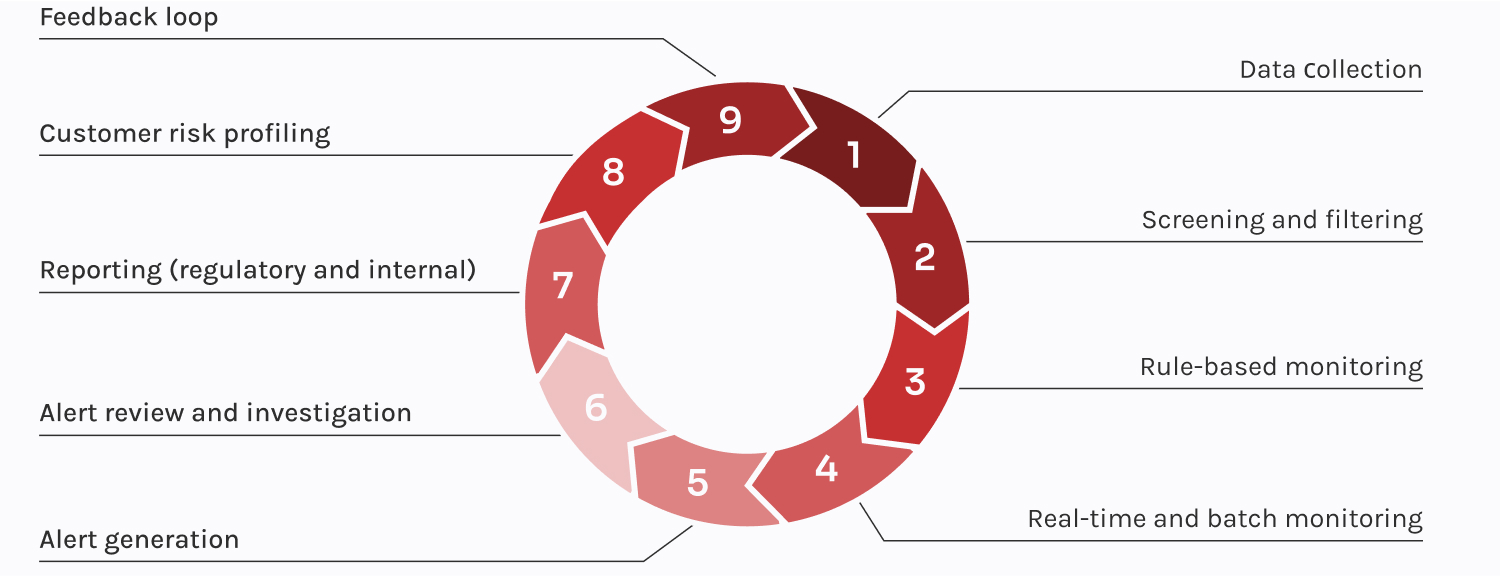
An AML transaction monitoring system should be built to scale and keep up with growing transaction volumes and complexity. It should also integrate effectively with your existing IT ecosystem for a smooth data flow and process automation.

Now that we’ve covered the basics of solid AML transaction monitoring systems and the red flags to watch for, let’s pull back the curtain and see how it all works. Here’s a step-by-step look at what’s happening behind the scenes.

Dzianis Kryvitski
Delivery Manager in Fintech
AML transaction monitoring is a powerful tool in the fight against financial crime that positively impacts every aspect of a business. Together, its benefits create a stronger, more secure ecosystem that safeguards operations and builds trust.
Businesses need to follow many regulations regarding AML, CTF, and fighting financial fraud. A strong AML transaction monitoring system helps you spot suspicious activity early and file reports on time, preventing penalties, costly audits, and potential restrictions on your business.
AML transaction monitoring helps assess exposure to various forms of financial crime and take proactive measures to reduce these risks. This is essential to a broader risk management strategy that helps strengthen your business’s overall financial stability and resilience.
Trust is vital in financial relationships, and if a business can’t detect suspicious activities, it can quickly lose that trust. AML transaction monitoring helps you build an image of a trusted partner, nurture customer loyalty, and avoid costly reputational consequences.
A solid AML transaction monitoring system handles tons of data automatically, cutting down on mistakes and saving you from wasting time on false positives. It lets your team focus on the real threats and prevents considerable resource drain.
AML transaction monitoring helps protect customers from identity theft, unauthorized transactions, and other forms of financial fraud. It creates a safer experience for clients and shows your commitment to safeguarding their financial well-being.
AML transaction monitoring helps keep the bank’s finances stable by flagging high-risk transactions and protecting its capital. It helps prevent cash flow disruptions caused by frozen assets, regulatory fines, or operational delays.
The massive amount of daily transactions makes banks a key target for money laundering. Criminals break up large sums, route funds through complex transfers, or hide illicit money using fake trade deals. AML solutions for banks quickly spot these red flags, ensuring compliance and safeguarding financial integrity.

With their fast-paced, high-volume transactions and minimal documentation, money transfer services are a magnet for financial crime. AML tools step in to catch irregular patterns, like small, repeated transfers or payments to high-risk regions, flagging them for further investigation.

Wealth and investment management firms handle complex portfolios, which makes them targets for financial crime. AML transaction monitoring flags investments linked to high-risk jurisdictions and detects portfolio irregularities to protect client assets and the firm’s reputation.

Loans can be a clever way to launder money — criminals use falsified documents, inflated credit scores, or questionable repayment patterns to funnel illicit funds. AML monitoring helps lenders weed out fake profiles and flag loans tied to high-risk sectors.

Currency exchanges are hotbeds for laundering, with criminals using rapid trades to clean dirty money. AML systems track trading patterns, catch suspicious fund movements, and flag accounts trying to dodge detection with small, frequent trades.

Criminals use cryptocurrency platforms for their speed and anonymity, shuffling funds across multiple wallets to cover their tracks. AML tools analyze blockchain activity, flag unusual wallet behavior, and screen wallets against sanctions lists to stop fraud in its tracks.

Brokerages face risks from money laundering schemes disguised as securities trading or market manipulation. Criminals can layer funds across accounts, trade illiquid assets, or inflate stock prices. AML systems catch unusual trading behaviors and block illicit activities before they escalate.

Insurance policies are an unexpected yet effective laundering tool for criminals. Overfunded policies, early surrenders for clean payouts, and fraudulent claims are common tactics. AML tools detect irregular premium payments, early cancellations, and claims tied to suspicious entities or individuals.

Legal firms aren’t immune — escrow services and client privileges can be misused to hide illicit funds. AML systems identify unusually high escrow deposits, track frequent ownership changes in deals, and help law firms stay compliant without compromising client trust.

To deal with money laundering effectively, AML can’t just play catch-up — it needs to get ahead of the game. The future of AML transaction monitoring will be defined by proactive, integrated approaches designed to tackle the challenges of increasingly sophisticated financial crime.
Intelligence-led risk management
Dynamic customer lifecycle management
Convergence of monitoring capabilities
Integrated data & tech infrastructure
Proactive and collaborative FIU
Integrated AML operations
Fighting financial crime is a never-ending battle. While we’ve learned a lot and built solid AML transaction monitoring solutions, staying ahead means being flexible, proactive, and taking a comprehensive approach. It’s the only way to keep your business safe, your transactions secure, and your customers protected.
Payment screening is a one-time pre-transaction process that checks payments against historical risk databases. In contrast, transaction monitoring is an ongoing process that analyzes post-transaction activities as well to detect broader suspicious behaviors.
KYC is key to spotting high-risk customers, like those tied to sanctions, politically exposed persons (PEPs), or shady industries. It also prevents identity theft and synthetic fraud by stopping criminals from using stolen or fake identities to exploit financial systems.
Each country has its own regulatory frameworks for AML, like the BSA and USA PATRIOT Act in the US or 5AMLD and 6AMLD in the EU. However, the main requirements remain consistent: risk-based monitoring, customer due diligence, and reporting suspicious activities to the relevant authorities.
AML transaction monitoring systems need regular updates to keep up with evolving financial crime tactics. Best practices recommend reviewing and updating these systems at least annually or whenever significant changes occur, such as new regulations, emerging risks, or shifts in customer behavior.










Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.