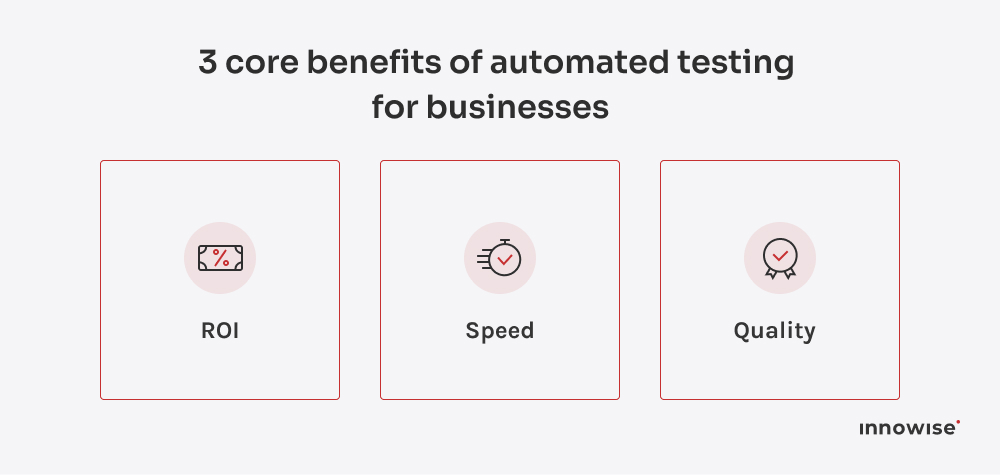
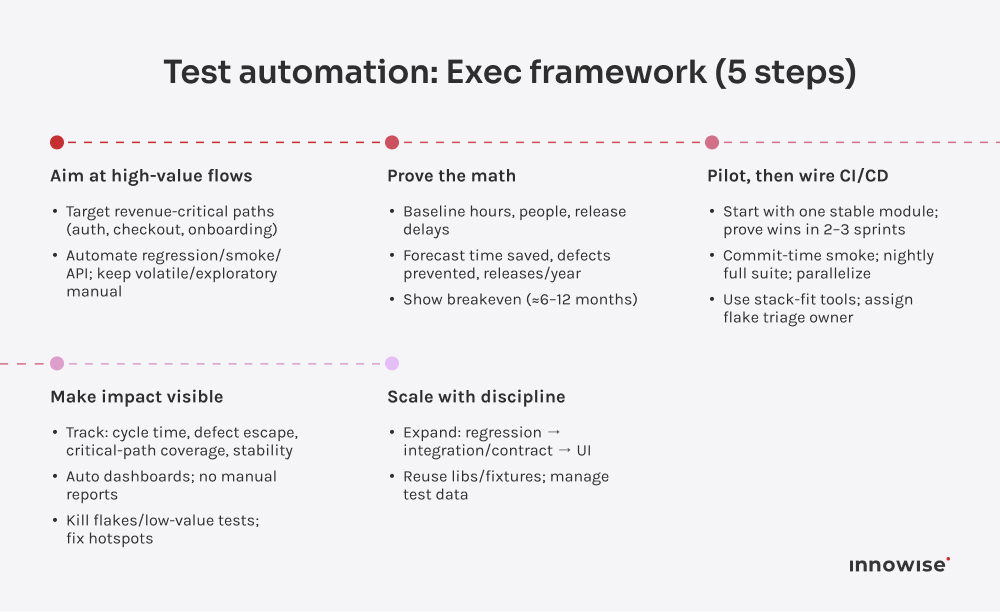
ROI in test automation comes from the time and cost saved by replacing repetitive manual work with continuous, automated testing. The breakeven point typically arrives within six to twelve months, depending on how frequently you release. Every subsequent sprint compounds the value: fewer regressions, faster deployments, and less QA overhead. Teams that measure consistently often see ROI exceed 200% as automation scales across projects and products.
Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.