Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.
The form has been successfully submitted.
Please find further information in your mailbox.


As the Head of Sustainability, I get asked this a lot: “What’s the difference between ESG and sustainability?” It’s a great question because, while closely connected, they serve different purposes and aren’t interchangeable.
Sustainability is the big-picture idea — a company’s long-term commitment to responsible practices that balance environmental care, social well-being, and economic growth. It’s about building a future where businesses thrive without compromising the planet or society.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG), is a specific framework used to measure and evaluate how well a company is performing in these areas. It focuses on metrics like carbon emissions, community engagement, and governance practices, offering stakeholders a clear way to assess impact.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the ESG vs sustainability debate — how these concepts differ, why they matter, and how businesses can leverage both to drive meaningful, lasting change.
annual growth in climate investments from 2019 to 2022
Source: McKinsey Sustainabilitycompensation will be tied to sustainable technology impact by 2027
Source: Gartnercompanies integrate ESG into their risk management processes
Source: RivelSustainability has always been about making the future more prosperous — meeting today’s needs without using up tomorrow’s resources. Its roots run deep, starting with socially responsible investing (SRI) in the 1970s, when investors began aligning their portfolios with their values. By the 1980s, corporate social responsibility (CSR) was in full swing, encouraging companies to give back to the planet and operate ethically. But while CSR got the ball rolling, it often lacked the necessary tools to measure real impact.
That all changed in the early 2000s. The “Who Cares Wins” report officially coined the term ESG (environmental, social, and governance), marking a shift toward measurable metrics and structured frameworks. Around the same time, organizations like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the UN’s Millennium Development Goals laid the groundwork for what ESG would become: a practical, action-oriented blueprint for businesses and investors.
ESG pushed eco-conservation into the spotlight, calling out issues like carbon emissions and resource use under its environmental pillar. The social component focused on labor rights, diversity, and community impact, while governance emphasized transparency and accountability. Together, these environmental, social, and governance pillars form a trifecta that now guides companies worldwide.
Fast forward to today, ESG is a global priority. Businesses are taking action, and investors are demanding results. From its early days as a niche idea to its current role as a turning point, ESG is about accountability, impact, and making a real difference.
Attract green investments with strong ESG performance.
Let’s face it — ESG and sustainability aren’t just trendy terms anymore. They’re the building blocks for how businesses stay relevant and earn trust. The way we work, the resources we use, and the impact we leave behind are under a global microscope. The United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), from fighting poverty to tackling climate change, give us a clear roadmap for the future. And guess what? Businesses play a starring role in this journey.
Here’s the thing: sustainability is a way of life, not a passing idea. Reducing emissions (think climate action, SDG 13) or creating fair opportunities (decent work and economic growth, SDG 8) doesn’t just help the planet, it also boosts your bottom line. Customers, investors, and employees are looking for companies that back their words with actions, and if you’re not on board, you’re already falling behind.
But this isn’t just about staying competitive. Regulations like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) are raising the bar. Starting in 2025, large EU-based companies meeting two of three criteria — more than 250 employees, revenues over €40 million, or assets exceeding €20 million — will need to report on their environmental and social impacts.
Sure, this might sound like a mountain to climb — collecting data, figuring out your value chain, and setting up systems can feel overwhelming. But here’s the silver lining: the companies that embrace sustainability today will be the ones leading the pack tomorrow. Think of greater risk management, stronger trust with stakeholders, and staying ahead of the curve in a world that’s changing fast.
This table offers a clear overview of the types of companies subject to ESG regulations and their respective reporting deadlines.
| Group | Criteria | Reporting year | Submission deadline |
| Organizations that were previously subject to the NFRD | >500 employees, €50M turnover, €25M assets | 2024 | 2025 |
| Large enterprises | >250 employees, €50M turnover, €25M assets | 2025 | 2026 |
| SMEs | 10+ employees, €900K turnover, €450K assets | 2026 | 2027 |
| Non-european companies | €150M EU revenue via subsidiaries/branches | 2028 | 2029 |
Today, sustainability isn’t optional — companies must back up claims with solid data and clear reporting. At the forefront are the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). These frameworks set the rules for how companies in the European Union report on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, treating sustainability with the same rigor as financial reporting.
Jozef Síkela, former Minister for Industry and Trade of the Czech Republic, explained, the CSRD was designed to drive real accountability: “The new rules will make more businesses accountable for their impact on society and will guide them towards an economy that benefits people and the environment. Data about the environmental and societal footprint would be publicly available to anyone interested in this footprint. At the same time, the new extended requirements are tailored to various company sizes and provide them with a sufficient transition period to get ready for the new requirements.”
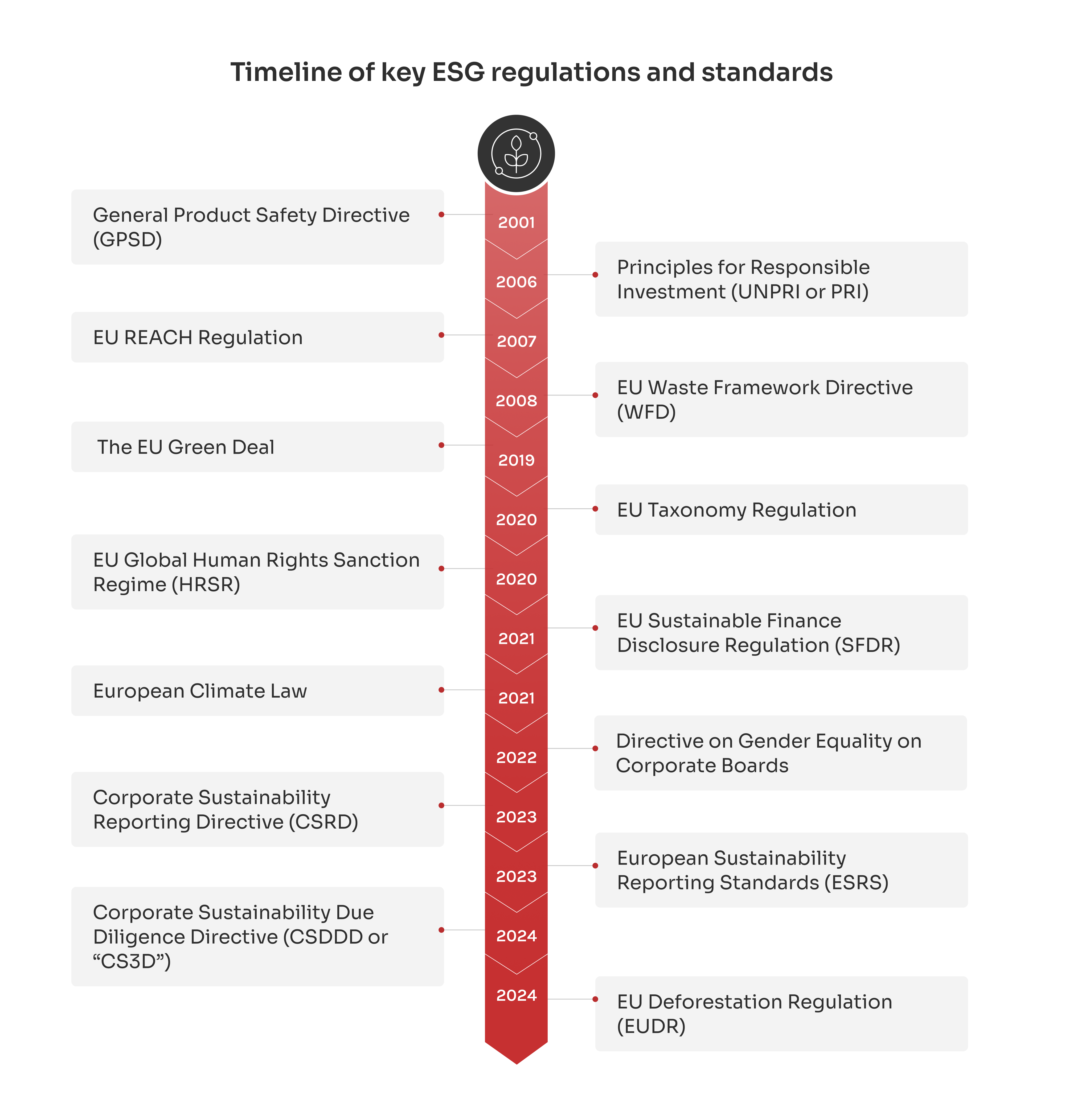
But these frameworks don’t emerge in isolation. They build on earlier EU regulations that lay the foundation for today’s comprehensive sustainability ecosystem. As we proceed, I’ll outline the key regulations that have shaped today’s ESG landscape and their implications for businesses operating in the European market.
The GPSD sets strict safety rules for products sold in the EU. Companies must test and verify that their products meet these standards before reaching consumers. If a product poses a risk, businesses must take action to fix the issue or remove it from the market.
The PRI, supported by the United Nations, is a global initiative promoting responsible investment. It provides a framework for integrating ESG factors into investment decisions, helping financial institutions align with sustainability goals.
The CSDDD pushes companies to take responsibility for their entire value chains. It requires businesses to identify, prevent, and address adverse human rights and environmental impacts — not just in operations, but across suppliers and partners.
The Waste Framework Directive (WFD) shifts the focus from managing waste to reducing it. The directive promotes recycling and reuse, encouraging companies to think in terms of circular economy principles.
The EU Green Deal lays out a plan to cut emissions and make Europe climate-neutral by 2050. It promotes clean energy, green industry, and economic policies that protect the environment while driving innovation.
The EU Taxonomy Regulation acts as the EU’s green rulebook. It defines what counts as a sustainable activity, helping investors identify genuinely green projects. This combats greenwashing and ensures sustainable investments are authentic.
The HRSR gives the EU a legal framework to sanction individuals and organizations involved in serious human rights abuses. This policy highlights that sustainability goes beyond the environment — it includes protecting people from exploitation and injustice.
The SFDR targets the financial sector, requiring firms to disclose how they integrate sustainability risks into investment decisions. It ensures that funds labeled as ‘green’ are genuinely sustainable, increasing transparency for investors.
The Law makes climate neutrality by 2050 a legal requirement, not just a goal. It holds EU institutions and member states accountable, with interim targets to track progress and uphold climate commitments.
By 2026, listed companies in the EU are expected to have at least 40% of non-executive director roles filled by the underrepresented gender, driving better business outcomes.
The CSRD elevates sustainability reporting to the same level as financial reporting, requiring companies to disclose detailed information about their environmental and social impacts, and how sustainability risks could affect their bottom line.
The ESRS sets clear rules for how companies report environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data. It creates a standardized approach, making it easier to compare sustainability efforts across industries.
The Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals regulation takes corporate responsibility further. It pushes companies to manage the chemicals they produce and use, focusing on environmental and human health impacts.
EUDR requires companies importing products like soy, beef, and palm oil to prove they are deforestation-free, strengthening the EU’s commitment to biodiversity and sustainable supply chains.
When we talk about the environmental aspect of ESG, it’s easy to focus only on carbon footprints. But it goes far beyond that. It’s about how we manage the resources we use, reduce waste, and protect biodiversity. This pillar pushes businesses to think critically about their entire environmental impact — from the energy powering their operations to the materials they source and how they dispose of them.
Take resource management, for example. Are you using water, energy, and raw materials efficiently, or is there room to cut back and save? Waste reduction is another key area. Every ounce of waste that doesn’t go to a landfill is good for the planet and great for reducing costs. And then there’s biodiversity — something businesses are just beginning to grasp. Protecting ecosystems is about the long-term health of supply chains and the communities that rely on them.
Thinking beyond carbon is where real leadership happens. Companies that do this are setting the standard for a truly sustainable future.
The “social” pillar of ESG is all about people. It’s about how businesses treat their employees, respect human rights, and contribute to the communities they serve. This pillar challenges us to look inward and ask some tough questions. Are workers treated fairly and paid equitably? Are safe working conditions a given or an afterthought?
But it doesn’t stop at the workplace. Human rights matter across the value chain, from the suppliers you work with to the customers you serve. And let’s not forget about community impact. Are you creating jobs, supporting local initiatives, and helping communities thrive?
The social pillar reminds us that businesses don’t exist in a vacuum. Companies that prioritize people — whether their own workforce or the broader community — are building stronger, more resilient organizations.
The “governance” pillar might not grab headlines like carbon reduction or community programs, but it’s the backbone of ESG. This is where businesses show their commitment to doing the right thing — every single day. It’s about transparency, ethics, and leadership.
Let’s start with transparency. Are you open about how decisions are made, how money is spent, and how risks are managed? Then there’s ethics. Do leaders actually do what they say when it comes to being honest and responsible? Board composition also plays a big role here. A diverse, skilled, and independent board is essential for making sound decisions and steering the company in the right direction.
Good governance is more than just avoiding scandals or ticking off regulatory boxes. It’s about building trust among investors, employees, and customers. Strong ethical leadership sets the tone for everything a business does, and when that’s in place, the rest tends to fall into line.

Dmitry Nazarevich
Chief Technology Officer
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles have become fundamental to how businesses create long-term value. Companies that integrate ESG into their core strategies are seeing tangible benefits, from operational efficiency and cost savings to stronger stakeholder relationships and competitive advantages in the marketplace.
Look at IKEA, they managed to shrink their climate footprint by 5% in just a year and a whopping 28% since 2016. How’d they pull that off? By doubling down on renewable energy, rethinking materials, and streamlining production. But it’s not just about the environment — IKEA’s big on community engagement too.
In Europe alone, IKEA carried out over 40 local activities, from volunteering and biodiversity projects to educational programs and circular economy initiatives. Whether it’s donating laptops to students in Indonesia or supporting children’s homes in Brazil, IKEA is making sure their impact goes beyond the bottom line.
Then there’s Microsoft, proving sustainability isn’t just for eco-brands. In 2023, they powered up with over 19.8 gigawatts of renewable energy across 21 countries. They’re also tackling water use head-on — designing data centers that don’t need water for cooling. Plus, they kept over 18,500 metric tons of waste out of landfills and are pushing suppliers to go 100% carbon-free by 2030. That’s not just good PR, it’s smart business that saves resources and future-proofs their operations.
And we can’t forget Unilever. They’ve gone all-in on sustainable sourcing, with 97.5% of key commodities like palm oil and soy coming from deforestation-free suppliers. They’ve slashed virgin plastic use by 18% since 2019 and are investing big in recyclable packaging. Consumers love it, investors love it, and it’s paying off in brand loyalty and market growth.
| Challenge | Issue | How to address it? |
| Dealing with different reporting standards | Companies often face overlapping ESG frameworks like GRI, SASB, and CSRD, creating reporting gaps and extra work. | It’s helpful to focus on the framework that aligns best with your industry and region. Consolidating data with ESG reporting tools can simplify the process and reduce duplication. |
| Keeping up with changing regulations | ESG regulations evolve quickly in the EU, UK, and US, making compliance an ongoing challenge. | Having a dedicated ESG team — whether in-house or outsourced — is crucial for staying on top of regulatory changes. Incorporating flexible reporting systems makes it easier to adapt quickly as new regulations are introduced. |
| Managing disconnected data | ESG data is often siloed across departments, leading to inconsistencies, errors, and reporting delays. | Centralizing ESG data on an integrated platform can improve consistency and accuracy. Automating data collection reduces manual errors and helps maintain real-time data availability. |
| Measuring ESG (environmental social and governance) impact | It’s often difficult to connect ESG initiatives to tangible business outcomes like cost savings or revenue growth. | Set clear ESG goals with measurable KPIs linked to business outcomes. Including these metrics in financial reports shows the real impact of sustainability efforts. |
| Defining ESG risks | ESG risks, like climate-related issues or reputational damage, are difficult to define and measure, leading to inconsistent risk assessments. | Clearly define ESG risks within your company’s risk management plan. Scenario analysis helps understand potential risks and make better decisions. |
| High costs of ESG implementation | ESG programs often require significant spending on technology, staff training, and data tools, which can strain budgets, especially for smaller companies. | You should focus on ESG activities that bring the most value to your business. Using scalable technologies and building partnerships can help manage costs while achieving strong results. |
Tired of keeping up with ever-changing ESG rules? Let us handle it for you.
As someone deeply involved in sustainability, I’ve seen how fast ESG is shifting from a “nice-to-have” to a business necessity. What was once a set of optional initiatives is now front and center in boardrooms, driven by global priorities, tech innovation, and rising expectations from investors, customers, and regulators. So, what’s next? Here are the key trends that will shape the future of ESG and sustainability.
The traditional “take-make-dispose” approach is quickly becoming outdated. More companies are shifting toward circular economy models, which focus on minimizing waste and making the most of resources. This means designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, while finding ways to reuse materials throughout the supply chain. It’s not just companies driving this change — government leaders are also recognizing the urgency of moving away from linear production.
As Linda Gillham, a UK local government councilor, points out, the “take-make-dispose” model is at the root of many environmental and social challenges. Tackling it is essential not just for building a sustainable economy but also for ensuring cleaner air, better food and water quality, and greater social equity.
ESG and sustainability are reshaping how businesses access capital. Green financing is on the rise, with investors increasingly favoring companies that demonstrate strong ESG performance. Instruments like green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and ESG-focused investment funds are becoming mainstream. Financial institutions are also tightening requirements, linking lending conditions to measurable ESG outcomes. For businesses, this means sustainability is no longer just a corporate responsibility issue — it’s a financial one, influencing creditworthiness and investment appeal.
What was once an ambitious goal is now becoming an expectation. Companies across industries are setting net-zero targets, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions as close to zero as possible, with any remaining emissions offset through carbon removal projects. But stakeholders are demanding more than just pledges — they want transparency, accountability, and real progress. This shift is pushing businesses to embed carbon reduction into every part of their operations, from supply chain management to product design and even employee commuting policies. The pressure is growing, and companies that fail to act risk falling behind both competitively and reputationally.
Technology is playing a pivotal role in advancing ESG efforts, making sustainability data more transparent, reliable, and actionable.
ESG and sustainability are quickly becoming must-haves for businesses everywhere. It’s no longer a question of if companies will report on their sustainability efforts, but when. Soon enough, transparent, data-backed reporting will be the norm. While some businesses still try to appear sustainable without real action (hello, greenwashing), the ones that will truly stand out are those delivering measurable, meaningful results.
At Innowise, we’re not here for empty promises — we’re here for results. We’ve built a strong ESG and sustainability practice, backed by real success stories. Whether it’s helping companies navigate ESG reporting or developing green solutions like sustainability-driven ERP and CRM systems, we’re all about making sustainability part of the business DNA. Our goal? To help businesses move beyond words and create lasting, positive change that truly makes a difference.













Your message has been sent.
We’ll process your request and contact you back as soon as possible.

By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy, including the use of cookies and transfer of your personal information.