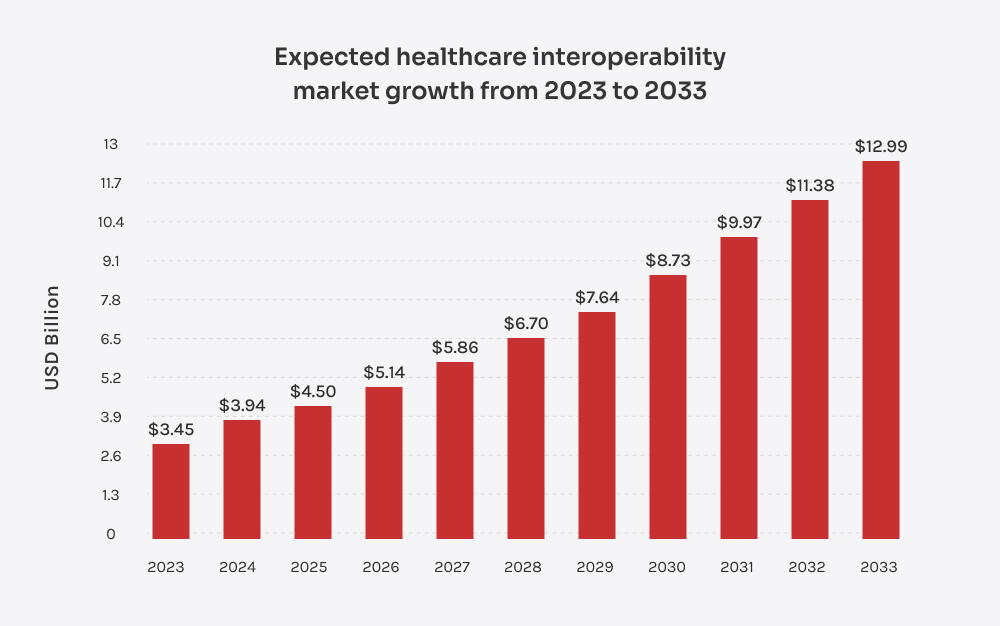
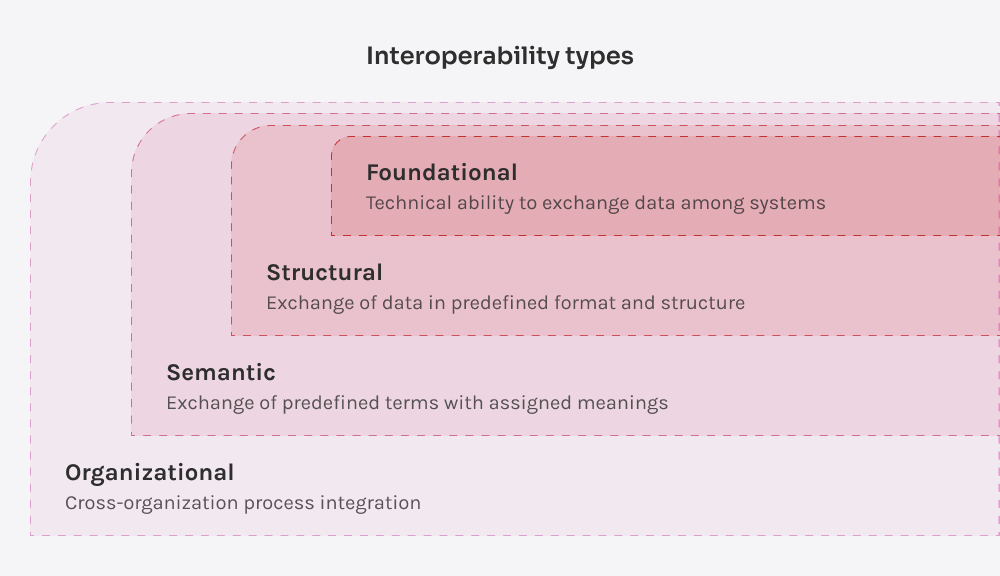
Improved patient outcomesData interoperability allows healthcare providers to access complete patient histories, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment plans. This seamless information exchange helps reduce errors and improves overall health outcomes.
Reduced costsWhen healthcare providers get complete patient data, they can avoid repetitive tests, procedures, and consultations. This not only saves time for patients and physicians but also reduces costs of care.
Enhanced care coordinationInteroperability allows multiple healthcare providers—like specialists, labs, and primary care doctors—to easily share patient information, leading to better, coordinated care. This reduces treatment gaps and ensures patients receive timely medical services.
Patient engagementWhen patients can access their health data through interoperable systems, they feel more in control of their healthcare decisions. This encourages active patient participation in care and improves health outcomes.
Public health and researchInteroperable data sharing enables the collection and analysis of vast amounts of health data, which can improve public health initiatives and drive research. This helps develop better treatment methods and policies that benefit entire populations.